Stepping into the complex realm of Payment Card Industry Data Security Standards (PCI-DSS) compliance can often seem intimidating, especially considering the numerous stringent rules and regulations involved. The article, “Understanding the Different Levels of PCI-DSS Compliance,” offers a comprehensive insight into this multifaceted discipline, guiding you through its labyrinthine matrix of regulations. It elucidates the various levels of compliance a business must strive to achieve depending on the number of transactions and the degree of risk associated. Your understanding of PCI-DSS compliance will inevitably deepen after reading the article, offering you a clearer direction on how to secure customer data efficiently and confidently.
Understanding PCI-DSS
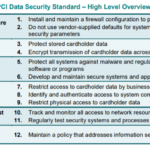
The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI-DSS) is a set of security standards created to manage and maintain a secure environment for all entities involved in the payment card industry. This includes merchants, financial institutions, point-of-sale vendors, and other service providers who are involved in the processing of cardholder data.
Definition of PCI-DSS
PCI-DSS is an acronym for Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard. This security standard was devised by the Payment Card Industry Security Standards Council to facilitate a safe and secure environment for all credit, debit, and cash card transactions. The standard contains a set of comprehensive requirements for enhancing the security of payment card data.
The importance of PCI-DSS
The PCI-DSS serves a crucial role in the protection of financial and personal information associated with card-based transactions. It helps businesses to securely handle cardholder information, reducing the risk of data breaches and thereby maintaining the confidentiality and integrity of payment card data. This standard is globally recognized and is critical for businesses to develop trust with their customers while ensuring secure financial transactions.
Who needs to comply with PCI-DSS
All entities that store, process or transmit cardholder data, including merchants and service providers, must comply with PCI-DSS. Standard compliance is not only required by major credit card companies but is also considered best practice for any business that deals with payment card information.
PCI-DSS Compliance Levels Explained
To better understanding PCI-DSS, it’s crucial to acquaint yourself with its levels of compliance, as these determine the extent and nature of the responsibilities that lie with you.
Description of PCI-DSS Compliance levels
There are four PCI-DSS compliance levels. Each level is determined by the number of transactions a merchant or service provider processes in a year. Level 1 represents the highest level involving more than 6 million transactions annually, while Level 4 is for businesses processing less than 20,000 transactions a year.
Factors determining the levels of compliance
The primary factor determining the compliance level is the total volume of credit card transactions processed annually. Other factors include the payment card brands processed, and whether the entity has suffered a breach or attack that resulted in an account data compromise.
Understanding risk levels associated with each compliance level
With each compliance level comes a different degree of risk. Higher compliance levels are given to entities processing a larger volume of transactions, and thus, they bear a higher risk of potential security breaches. Lower levels signify reduced risk, as they deal with fewer transactions, yet they are nonetheless obligated to maintain a secure environment.
Level 1 PCI-DSS Compliance
As the highest level of compliance, Level 1 is associated with stringent requirements and a significant level of responsibility associated with transaction processing.
Explanation of Level 1 Compliance
Level 1 compliance applies to merchants and service providers that process over 6 million card transactions annually across all channels including ecommerce, mail/telephone, or face-to-face environments.
Who needs Level 1 Compliance
Entities processing more than 6 million card transactions each year are required to meet Level 1 PCI-DSS compliance. These can be large retail companies, financial institutions, and other high-volume transaction entities.
Requirements for achieving Level 1 Compliance
To achieve Level 1 compliance, entities are required to undergo an annual on-site PCI Data Security Assessment by a Qualified Security Assessor (QSA) or a firm-specific Internal Security Assessor (ISA). Additionally, they must conduct a quarterly network scan by an Approved Scanning Vendor (ASV).
Level 2 PCI-DSS Compliance
One level down from the highest, Level 2 compliance is associated with a moderate transaction volume.
Explanation of Level 2 Compliance
Merchants processing 1 to 6 million transactions annually are categorized under Level 2 PCI-DSS compliance.
Who needs Level 2 Compliance
Medium to large-sized businesses processing between one to six million transactions annually need to comply with Level 2 requirements.
Requirements for achieving Level 2 Compliance
The requirements for achieving Level 2 compliance are primarily self-assessment wherein a Self-Assessment Questionnaire (SAQ) has to be completed annually. Along with this, an undertaking has to be made confirming that the merchant is compliant with the PCI-DSS. Another mandatory requirement is the quarterly network scan by an ASV.
Level 3 PCI-DSS Compliance
Level 3 deals with a lower level of transactions but still requires comprehensive attention to security.
Explanation of Level 3 Compliance
Level 3 compliance applies to merchants that process 20,000 to 1 million transactions annually.
Who needs Level 3 Compliance
Medium and developing businesses that process 20,000 to 1 million transactions per year may need to meet Level 3 PCI-DSS compliance.
Requirements for achieving Level 3 Compliance
The requirements for Level 3 compliance involves a self-assessment questionnaire, an ASV quarterly network scan, and an Attestation of Compliance (AOC) form.
Level 4 PCI-DSS Compliance
Level 4 is the lowest level in terms of transaction volume, but it does not diminish the importance of complying with PCI-DSS standards.
Explanation of Level 4 Compliance
Level 4 applies to merchants that process less than 20,000 transactions annually.
Who needs Level 4 Compliance
Small businesses or merchants who process less than 20,000 card transactions annually fall under this compliance level.
Requirements for achieving Level 4 Compliance
For Level 4 compliance, the same requirements apply as with Level 3 compliance. This involves completion of the SAQ, quarterly network scans by an ASV, and if applicable, completing the relevant Attestation of Compliance (AOC).
Understanding PCI-DSS Compliance Assessment
A PCI-DSS Compliance Assessment is a thorough examination of an entity’s adherence to the PCI-DSS standards.
The process of PCI-DSS Compliance Assessment
The assessment involves scrutinizing the entity’s cardholder data environment, reviewing security policies, procedures, network architecture, software design, and security systems and processes.
Who conducts the PCI-DSS Compliance Assessment
PCI-DSS Compliance Assessment is conducted by a Qualified Security Assessor (QSA)– a firm that is independently certified by the PCI Security Standards Council.
Timeframes for PCI-DSS Compliance Assessment
The time frame for a PCI-DSS Compliance Assessment may vary based on the size and complexity of the cardholder data environment. However, to maintain compliance, the assessment should be conducted annually and the ASV scans, quarterly.
Benefits of PCI-DSS Compliance
Beyond the mandatory requirement, compliance with PCI-DSS confers various benefits to an entity.
Protecting business reputation
Compliance supports the protection of the entity’s reputation by demonstrating to consumers that the entity operates in a secure way and that their financial data is safe.
Avoidance of non-compliance penalties
Non-compliance can result in significant financial penalties imposed by credit card companies. By complying with PCI-DSS, entities can avoid such penalties.
Enhanced customer trust
Compliance enhances customer confidence and trust, as it reassures consumers that their sensitive information is securely handled.
Penalties for Non-Compliance of PCI-DSS
Non-compliance with PCI-DSS can result in severe consequences for entities.
Different types of PCI-DSS non-compliance penalties
Non-compliance penalties can take the form of monetary fines, increased transaction fees, or, in severe cases, termination of the ability to accept card payments.
The process of penalty determination
Penalties are usually determined by the credit card brands based on the level of non-compliance and the number, size, and resulting damage of any data breaches.
Potential impact of non-compliance
The impact of non-compliance can compromise business operations and revenue. Non-compliance can tarnish brand reputation, cause loss of customer confidence, and lead to considerable financial penalties.
Navigating PCI-DSS Compliance Audits
PCI-DSS compliance audits are necessary to verify that PCI-DSS standards are being meet and maintained.
The role of a PCI-DSS Compliance Auditor
A PCI-DSS Compliance Auditor’s role is to evaluate the entity’s practices, systems, and procedures to ensure they are in compliance with the PCI-DSS standards.
Preparing for a PCI-DSS Compliance Audit
Preparation for an audit includes reviewing security controls in place, fixing any vulnerabilities, compiling relevant documentation, and making certain that all practices are compliant with the PCI-DSS standards.
Understanding the Possible Audit Outcomes
Audit outcomes can range from validation of full compliance, through to identification of areas that need improvement, to reporting of major non-compliance issues. Depending on the findings, a plan may be required to address any areas of non-compliance.
In conclusion, understanding PCI-DSS and its different levels of compliance is crucial for every entity that deals with payment card transactions. Being aware of your entity’s compliance level, undergoing regular assessments, and maintaining an ongoing commitment to the security practices outlined in the PCI-DSS standard, are all essential parts of maintaining the integrity of cardholder data and the security of the overall payment card industry.