In the currency of today’s digital information age, data, specifically cardholder data, has become a critical asset that demands rigorous protective measures. The indispensable guide, “Controlling and Monitoring Access to Cardholder Data: A Comprehensive Guide”, offers extensive knowledge on effective strategies and protocols aimed at safeguarding sensitive payment card information. With a key focus on control measures and real-time monitoring methodologies, this guide allows you to comprehend and implement the most secure practices in relation to cardholder data access. It sheds light on how access to cardholder data, a potential treasure trove for cybercriminals, should be managed with calculated precision and unwavering vigilance.
Understanding Cardholder Data and its Importance
In dealing with commercial transactions, particularly in the digital age, one form of data is of importance – cardholder data. This category of data, which often includes details such as the cardholder’s name, account number, expiration date, and service code, is crucial for completing financial transactions using credit and debit cards.
Defining Cardholder Data
Cardholder data is essentially every piece of information contained on or linked to a payment card, such as credit and debit cards. This data is the foundation of all card-based transactions and is integral to the functioning of the global commerce system. For a transaction to be completed, the cardholder’s name, card number, expiration date, and security code are often required at a minimum.
Relevance of Secure Cardholder Data
Information security plays a critical role in maintaining trust and integrity in the digital marketplace. This is especially true for cardholder data. If this information is not adequately secured, sensitive data can be compromised, potentially leading to unauthorized transactions – putting both businesses and customers at risk. Keeping cardholder data secure not only helps safeguard your business’s financial resources but also builds trust with your clients by showcasing your commitment to data security.
Potential Risks of Unguarded Cardholder Data
Inadequate security of cardholder data can lead to many issues, including financial loss, damage to brand reputation, and possible legal repercussions. Information fraud and identity theft are potential direct outcomes if this sensitive information lands in the wrong hands. For businesses, this could lead to a loss of customer trust and loyalty, which in turn could impact revenue and reputation in the market.
Determining Who Needs Access to Cardholder Data
It’s crucial to establish strict controls on who within your organization has access to cardholder data. This restricts the data’s exposure to a minimum number of individuals and reduces the risk of internal compromise.
Defining Roles and Responsibilities
The first step in securing cardholder data is to clearly define roles and responsibilities within your organization. This helps everyone understand who has access to the data and the extent of that access. It is usually the responsibility of individuals in key positions such as system administrators, financial controllers, and certain managerial staff to handle cardholder data.
Assessing the Needs and Limits of User Access
Once roles have been firmly defined, the next step is to determine the need and limit of access for each role. It may be tempting to grant everyone access to all data, but this is a recipe for disaster. Instead, the principle of “least privilege” should be applied, where individuals only have access to the data they need to fulfill their job duties and no more.
Allocating Access Rights to Authorized Personnel
Managing access rights effectively requires creating a policy that outlines which roles can view, edit, or otherwise interact with cardholder data. This keeps data secure by limiting access to only those who have a genuine business need for it.
Implementing Access Control Measures
While determining who should have access to cardholder data is critical, implementing stringent access control measures is just as important for ensuring the security of such sensitive information.
Deploying Password Protection Procedures
The implementation of strong password protection procedures is the first line of defense in securing access to cardholder data. The use of robust, unique passwords is encouraged, as is the regular changing of these passwords. Furthermore, the use of multi-factor authentication introduces an additional layer of security.
Setting Up Firewall Applications
Firewalls provide a critical control point for traffic filtering between trusted and untrusted networks and are an essential tool for any organization’s data protection toolkit. Their ability to block unauthorized access while allowing sanctioned communication ensures that your organization’s critical data is always protected.
Establishing System Authentication and Authorization
System authentication and authorization are crucial to ensure that only approved and authenticated users can access your systems. This involves the implementation of tools and procedures such as user credentials, role-based access control, and multi-factor authentication.
Implementing System-Level Permissions
Setting up system-level permissions allows you to designate what users can do once they have access to your system. These restrictions can help make sure that individual users can only conduct activities pertinent to their designated role, further reducing the risk of accidental or deliberate misuse of cardholder data.

Securing Physical Access to Data
While focusing on online or digital threats, it is vital not to overlook the physical security. The storage and physical handling of cardholder data must be addressed to ensure full data protection.
The Importance of Physical Security
Physical security is crucial. A simple theft of documents or a hardware device could result in substantial data breach. Every business must ensure adequate security measures are in place to prevent unauthorized physical access to cardholders’ sensitive data.
Secure Storage Locations for Cardholder Data
The safe storage of physical hardware, files, and documents containing cardholder data is a must. This could include secure filing cabinets, safes, or even dedicated secure rooms. The ultimate aim is to ensure that only authorized personnel can gain physical access to these data storage locations.
Security Measures for Physical Access
Deploying physical security measures such as locks, access cards, and even security personnel can significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access to data. Additionally, the use of surveillance systems like CCTV can provide an extra level of security.
Use of Encryption for Protecting Cardholder Data
Encryption is one of the most effective ways to keep cardholder data secure, ensuring that the data, even if intercepted, remains unintelligible to unauthorized parties.
Introduction to Data Encryption
Data encryption is the process of translating data into another form so that only authorized parties with a decryption key can read it. It is one of the leading defenses against data breaches, ensuring that even if data falls into the wrong hands, it remains inaccessible.
Implementing Encryption Solutions
Numerous encryption solutions are available, each offering different levels of security. Some commonly used approaches involve encrypting the entire database or using field-level encryption for specific sensitive data like cardholder data. Ultimately, the ideal encryption solution depends on your organization’s specific needs.
How Encryption Strengthens Cardholder Data Security
Implementing encryption solutions greatly enhances cardholder data security. Even in the event of a system compromise, encryption helps ensure that the cardholder data remains inaccessible as long as the decryption keys are tightly controlled.
Monitoring and Logging Access to Cardholder Data
Continuous monitoring and logging access to cardholder data is crucial to promptly detect and respond to any potential data breach incidents.
Need for Continuous Monitoring
Continuous monitoring ensures that you are always aware of who is accessing cardholder data and what changes are being made. This heightened visibility allows quick detection of abnormalities and swift response to any potential security challenges.
Effective Use of Logging and Reporting Tools
Utilizing logging and reporting tools can provide invaluable insights into system usage patterns. This can help identify anomalies, signs of potential system compromise, or unauthorized access attempts.
Identifying Suspicious Activities
Monitoring systems should be equipped to identify suspicious activities such as multiple unsuccessful login attempts, unusual user behavior, or irregular transaction patterns. Early detection of these activities is critical in thwarting potential security incidents.
Incident Response Planning
Despite your best efforts, the reality is that no system is 100% secure. Having an incident response plan ready can significantly reduce the damage caused by a data breach.
Developing an Incident Response Process
An incident response process should outline the steps to be followed in the event of a data breach. The process should involve identifying the incident, containing the breach, eradicating the threat, recovering from the incident, and then conducting a post-incident review.
Preparing for Possible Data Breach Incidents
Preparation is crucial to managing potential data breach incidents. Regular incident response drills or exercises can help ensure that your team is ready to respond quickly and efficiently when required.
Response and Recovery after an Incident
In the unfortunate event of a data breach, the ability to respond swiftly and recover as quickly as possible is essential. This could involve isolating affected systems, identifying the breach source, and patching vulnerabilities. Post recovery, it’s important to analyze the incident and modify your security measures appropriately to prevent a recurrence.
Training and Awareness Programs
Human error can often be a significant risk in data security. Conducting regular training and awareness programs can help mitigate this risk by educating staff about security best practices.
Creating Awareness about the Importance of Cardholder Data Security
Organizations should place emphasis on creating awareness among employees about the importance of cardholder data security. This can be achieved through regular engagement, discussions, and workshops, emphasizing why safeguarding cardholder data is integral to them and the organization.
Training Staff on Security Policies and Best Practices
Training sessions should encompass the organization’s security policies and best practices related to handling cardholder data. These sessions should detail how to recognize and handle potential threats and should extend to all staff, not just those who directly handle cardholder data.
Regular Updates and Refresher Courses
Cyber threats evolve constantly, as do technology and regulations. Therefore, it’s critical to arrange regular updates and refresher courses for your staff to keep them abreast of the latest trends, threats, and mitigation strategies in data security.
Regular Audits and Compliance
Regular audits and demonstrating compliance with security standards are integral components of an effective data security strategy.
Purpose of Regular Audits
Regular audits help to ensure continuous compliance with security measures and provide insights into any potential security vulnerabilities. It’s essential to identify and address these weak spots before they can be exploited.
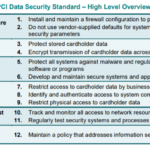
Ensuring Compliance with PCI DSS
The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) is a set of security standards designed to protect cardholder data. Companies that handle such data must adhere to these standards. Regular audits help ensure continuous compliance with these regulations and help foster trust with customers and stakeholders.
Remediation Plans for Non-Compliance
In instances where non-compliance is identified during audits, a remediation plan should be created and executed quickly to address those issues. Failure to comply with standards like PCI DSS can lead to penalties and can damage your organization’s reputation.
Keeping Access Control Systems Updated
Security solutions have an expiry date. As potential threats evolve, so does the technology designed to combat them. Keeping your systems updated is thus pivotal in maintaining a strong security posture.
The Need for Regular Software Updates
Regular software updates provide critical patches, bug fixes, and other enhancements that elevate system defenses and mitigate the risk of data breaches. Delay in applying these updates provides opportunities for cybercriminals to exploit these vulnerabilities.
Incorporating New Security Features
As technology evolves, new security features and tools become available. These enhancements can significantly bolster your security posture, providing protection from emerging threats. Regularly updating your systems helps ensure that you are making the best use of the tools available to you.
Preparing Your Systems and Staff for Updates
While most software updates are straightforward, some may require significant changes to your systems or processes. It’s important to prepare your systems and provide any necessary staff training to minimize disruptions.
In conclusion, controlling and monitoring access to cardholder data requires a comprehensive approach with multiple layers of security measures. The importance of maintaining robust security controls cannot be understated, given the sensitive nature of cardholder data and the potential ramifications of any breach. By focusing on understanding cardholder data and its importance, determining who needs access, implementing access control measures, securing physical access to data, using encryption for protection, monitoring and logging access, planning for incident response, conducting training, ensuring compliance, and keeping systems updated, you can significantly enhance the security of your cardholder data.