In a digital era that’s witnessing an unprecedented rise in cryptocurrency transactions, comprehending the role and significance of PCI-DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard) has become essential. The article named “Understanding the Application of PCI-DSS in Cryptocurrency Payments” unravels this relationship, offering a deep insight into how PCI-DSS standards apply to cryptocurrency payments. This write-up critically examines the adaptation of PCI-DSS standards to ensure secure, compliant and efficient crypto transactions, thereby illuminating the path towards secure digital financial exchanges worldwide.
This image is property of 2muchcoffee.com.
Understanding PCI-DSS
Definition and purpose of PCI-DSS
The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI-DSS) is a security standard with established guidelines to protect card transactions against data theft and fraud. Utilized globally, it ensures that businesses that carry out transactions using credit or debit cards maintain a secure environment. The key purpose of PCI-DSS is to ensure protection of sensitive data, thereby reducing the likelihood of data breaches.
History and evolution of PCI-DSS
The development of PCI-DSS began in 2004 when five major credit card networks, Visa, Mastercard, JCB, Discover, and American Express, joined forces. The goal was to create a universal standard to address the rampant card data threats, replacing individual company regulations. With time, the security requirements of PCI-DSS have been revised and augmented to cope with the escalating sophistication of cyber-attacks.
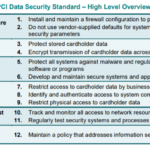
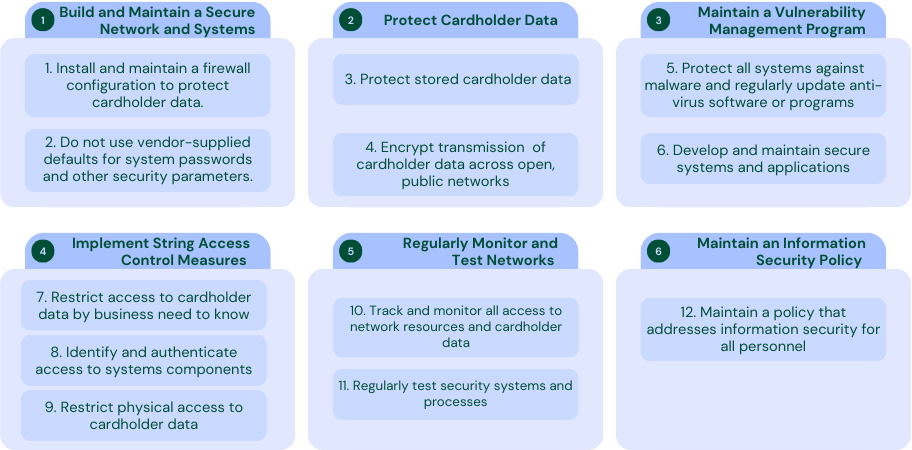
Overview of the 12 requirements of PCI-DSS
The PCI-DSS is comprised of 12 key requirements divided into six overarching goals. These include creating and maintaining a secure network, protecting cardholder data, maintaining a vulnerability management program, implementing firm access control measures, auditing& monitoring of network resources, and sustaining an information security policy.
Understanding Cryptocurrency Payments
Definition and concept of Cryptocurrency
A cryptocurrency is a digital or virtual form of currency that employs cryptography to secure transactions and control the flow of new units. Cryptocurrencies function on decentralized systems known as blockchain technology. Popular as a disruptive financial technology, it offers alternative forms of payments that are independent of centralized banking networks.
History and evolution of Cryptocurrency
Motivated by the global financial crisis of 2008, the inception of cryptocurrency began with Bitcoin, introduced by an individual or group under the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto. Since then, the world has seen an explosion of various cryptocurrencies, with thousands currently existing. The growing acceptance of cryptocurrency as a viable financial system has transformed the way financial transactions are conducted.
Understanding how Cryptocurrency payments work
Cryptocurrency payments work by utilizing blockchain technology which records and validates every transaction across a decentralized network of computers. When a transaction is initiated, it is broadcasted to the network where validators approve it. Payments are processed without the need for an intermediary, and transactions are irreversible once confirmed.
Risks associated with Cryptocurrency payments
While cryptocurrency provides an alternative financial transaction system that mitigates some traditional banking risks, it does have its risks. These include vulnerability to hacking, extreme price volatility, lack of regulatory oversight, and potential for use in illegal activities.
PCI-DSS in Relation to Cryptocurrency Payments
Role of PCI-DSS in safeguarding Cryptocurrency transactions
Although cryptocurrency transactions are not traditional card transactions, applying PCI-DSS practices to them provides additional layers of security. PCI-DSS requirements such as maintaining a secure network, protection of sensitive data, and regular monitoring can help mitigate cryptocurrency-related risks by providing a systematic protocol for safeguarding transaction data.
Challenges of applying PCI-DSS to Cryptocurrency payments
The decentralized nature of cryptocurrency adds complexity to the application of PCI-DSS protocols. The absence of a central authority limits the enforcement of standard security practices. Furthermore, the reversibility of transactions presents another challenge. Once a cryptocurrency transaction is confirmed, it cannot be undone, unlike card transactions that can be disputed and reversed.
Possible solutions to these challenges
While challenges exist, potential solutions include adopting a regulatory framework for cryptocurrencies that parallels the PCI-DSS guidelines and encouraging cryptocurrency platforms to comply voluntarily. Blockchain technology could also be tailored to allow for dispute resolution and reversal of fraudulent transactions.
The Applicability of PCI-DSS Requirements in Cryptocurrency
Understanding how each PCI-DSS requirement applies to Cryptocurrency
While PCI-DSS was not designed for cryptocurrencies, its principles can be adapted. For instance, creating and maintaining a secure network can be achieved by encrypting and regularly updating cryptowallets, and monitoring access to these wallets.
In-depth discussion on the challenges in implementing each requirement
Challenges include the irreversibility of transactions, lack of effective authority for dispute resolution, variances in security practices across different cryptocurrency platforms, and technological constraints in implementing some PCI-DSS requirements.
This image is property of miro.medium.com.
Legislative and Regulatory Challenges of PCI-DSS in Cryptocurrency
Explaining the legislative constraints
Legislative constraints include an absence of universal regulatory standards for cryptocurrencies and jurisdictional variances in cryptocurrency regulations. Further, legal recognition of cryptographic tokens and private keys as forms of ownership also poses challenges.
Overview of regulatory issues in applying PCI-DSS to Cryptocurrency
Regulatory issues include a lack of established protocol for the enforcement of PCI-DSS compliance by cryptocurrency platforms. Other issues are the variability in security standards across platforms and resistance to regulation from some parts of the cryptocurrency community.
Benefits of Applying PCI-DSS in Cryptocurrency Payments
Enhancement of security in Cryptocurrency transactions
Applying PCI-DSS standards to cryptocurrency payments can augment security by ensuring secure storage and transmission of transaction data. This can drastically reduce the risk of data breaches and fraudulent activities.
Boosting of trust and confidence among Cryptocurrency users
With enhanced security, trust and confidence among cryptocurrency users are likely to grow. This promotes broader acceptance and usage of cryptocurrencies for transactions.
Prevention of potential fraud and theft in Cryptocurrency
PCI-DSS can provide structured procedures to identify and address potential security threats in real-time, preventing fraud and theft.
This image is property of www.investopedia.com.
Case Studies on the Application of PCI-DSS in Cryptocurrency
Image of the real-world application of PCI-DSS in Cryptocurrency
Case studies showcasing successful applications of PCI-DSS principles provide learning opportunities and demonstrate the viability of integrating PCI-DSS in cryptocurrency transactions.
Reflections and lessons learned from each case study
Each case study offers unique insights into the challenges and solutions of implementing PCI-DSS, and how cryptocurrency firms can adapt these lessons to their specific context.
Future Trends of Applying PCI-DSS in Cryptocurrency
Anticipating changes in Cryptocurrency that may affect PCI-DSS
Understanding future trends in cryptocurrency is crucial to adapt and evolve PCI-DSS to ensure it remains relevant and effective in guarding against threats.
Preparing for future security needs in the Cryptocurrency sector
Keeping pace with technological innovations and regulatory changes is key in building robust security models that blend the benefits of PCI-DSS with the unique security needs of Cryptocurrency.
This image is property of i0.wp.com.
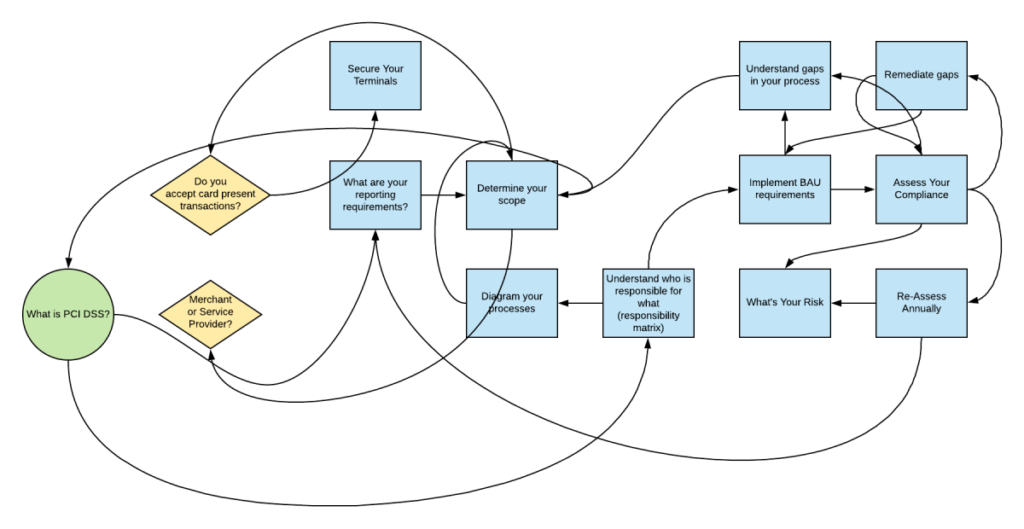
Planning a PCI-DSS Compliance Strategy for Cryptocurrency Payments
Identifying the key components of a good strategy
A good strategy would necessitate a risk assessment, identification of security objectives, assignment of responsibilities, development of incident response plan, and ongoing monitoring and updates.
Steps to designing and implementing the strategy
The primary steps include identifying the scope of the strategy, defining the security objectives, developing procedures and guidelines and executing the strategy. Thereafter, monitoring compliance, inconsistencies, and incidents and adjusting the strategy as required are necessary steps to ensure continuous effectiveness.
Best practices for maintaining PCI-DSS compliance
Best practices would involve regular risk assessments, maintaining security procedures and policies, providing employee training, implementing robust access control measures, using secure tools and systems and continuously evaluating and improving the compliance program.
Conclusion
Summarizing the role and importance of PCI-DSS in Cryptocurrency payments
PCI-DSS can play a significant part in enhancing the security of cryptocurrency payments. While challenges persist, it offers a structured approach to risk management and data protection in the growing field of cryptocurrency.
Recap on the challenges and solutions in applying PCI-DSS
Application of PCI-DSS in the decentralized and complex world of cryptocurrency does present challenges. However, drawing from experiences and exploring possible solutions can aid in overcoming these hurdles.
Propose recommendations for future research and policy
Future research should investigate ways to modify the PCI-DSS framework to better fit the unique characteristics of cryptocurrency. Regulatory policies must look into the potential of integrating PCI-DSS into the legislative frameworks for cryptocurrency to enhance global transactional security.