In “Understanding What is Involved in a PCI-DSS audit“, you will find a focused exploration into the intricacies of PCI-DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard) audits. This article is crafted to provide you with an intricate understanding of this complex procedure, navigates through the regulatory requirements, and expounds on the significant role it plays in securing cardholder data globally. Grasping this procedure’s intricacies will empower you with essential resources to aid your enterprise in maintaining compliance and ensuring data security, an increasingly crucial aspect in today’s digital business landscape.
Understanding PCI-DSS
When it comes to secure payment processing, a crucial aspect to understand is the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI-DSS).
Definition of PCI-DSS
PCI-DSS is a security standard for organizations that handle card payment transactions. Established by the PCI Security Standards Council, the PCI-DSS spells out measures to ensure that cardholder data is stored, processed, and transmitted securely.
Importance of PCI-DSS
In the face of escalating cyber threats, PCI-DSS plays a critical role in enhancing card data safety. Adopting PCI-DSS not only minimizes the risk of data breaches but also cultivates customer confidence. Thus, organizations not only avoid penalties associated with non-compliance but also reap the benefits of customer trust and loyalty.
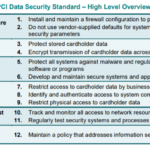
Overview of PCI-DSS standards
The PCI-DSS consists of twelve primary requirements grouped into six categories, including; building and maintaining a secure network, protecting cardholder data, maintaining a vulnerability management program, implementing robust access control measures, regularly monitoring, and testing networks and maintaining an information security policy.
Purpose of a PCI-DSS Audit
Organizations need to be audited for PCI-DSS compliance to ensure they meet the requirements of the standard.
The importance of auditing for compliance
Auditing for compliance is essential to confirm that your organization’s systems, procedures, and controls align with the PCI-DSS requirements. Regular compliance audits provide assurance that a company’s data preventive measures are robust and up to date, thereby minimizing the risk of breaches.
Meeting legal and business requirements
An audit assures that your organization fulfills legal obligations, as failure to comply with the PCI-DSS can result in hefty fines and penalties. Additionally, PCI compliance can be a requirement for conducting business with some partners and clients, making the audit indispensable.
Protecting customer data
The ultimate goal of a PCI-DSS audit is to protect customer data. The audit assesses the efficacy of the implemented measures to secure cardholder data, which, when adequately protected, enhances customer trust and loyalty.
Types of PCI-DSS Audits
There are several types of audits your organization can undergo to comply with PCI-DSS.
Self-Assessment Questionnaire
A Self-Assessment Questionnaire (SAQ) is designed for organizations that are not required to undergo an onsite audit. It is a tool that helps such businesses gauge their compliance with PCI-DSS.
Onsite PCI-DSS Audit
An onsite audit is conducted by an Official PCI Security Standards Council Qualified Security Assessor (QSA). They assess the organization’s security infrastructure against the PCI-DSS requirements for compliance.
Network Security Scan
Organizations are required to perform quarterly network security scans. This involves externally scanning all IP addresses within the organization that can potentially affect the security of the cardholder data environment.
Penetration Testing
Penetration testing is another mandatory component of PCI-DSS compliance, designed to identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses in the network that hackers might exploit.
Preparation for a PCI-DSS Audit
Preparing for a PCI-DSS audit involves several steps, including defining the scope, performing a gap analysis, gathering data, and risk assessment.
Understanding the audit scope
The audit scope entails establishing the environment within your organization where cardholder data is stored, processed, or transmitted, which falls under the purview of the PCI-DSS.
PCI-DSS Gap Analysis
A Gap Analysis helps to identify and understand areas where your organization does not meet PCI-DSS requirements. This analysis helps to develop a remediation plan to address those gaps, serving as a step towards compliance.
Pre-audit data gathering
This stage involves gathering the necessary documentation that evidences your compliance efforts. These documents may include firewall settings, encryption methods, incident response plans, and policy and procedure documentation.
Risk Assessment
The risk assessment process helps identify and assess risks that can impact the security of cardholder data, providing insights into potential areas that need attention during the audit.
The PCI-DSS Audit Process
The audit process involves several stages, including documentation review, personnel interviews, system and network analyses, and operational process observation.
Review of documentation
This entails analyzing all the documents related to the cardholder data environment. These documents outline the policies and procedures that ensure data protection.
Interviews with Key Personnel
The assessor may conduct interviews with relevant personnel like system administrators or network engineers to ascertain the nature of procedures and controls in place.
System and Network Analysis
An in-depth technical assessment of the systems and network infrastructure helps to establish whether they meet PCI-DSS requirements. The analysis also identifies any existing vulnerabilities.
Observing Operational Processes
Observation of operational processes and procedures helps ascertain their adherence to the stipulated PCI-DSS requirements in real-time situations.
Post-Audit Activities
After the audit, there are several activities that should be undertaken, including interpretation of findings, development of action plans, and addressing non-compliance issues.
Interpretation of audit findings
Interpreting the audit findings involves understanding the issues and gaps identified during the audit. This information is critical in planning the next steps towards compliance.
Developing an action plan
Based on the audit findings, an action plan should be developed to address the identified issues. This plan provides a clear roadmap towards achieving and Maintaining PCI-DSS compliance.
Addressing non-compliance issues
If the audit uncovers areas of non-compliance, these issues must be promptly addressed to prevent possible data breaches and avoid regulatory fines and penalties.
PCI-DSS Audit Report
The audit report formalizes the findings of the audit process.
Types of audit reports
There are different types of PCI-DOS audit reports, including the Report on Compliance (ROC) for level 1 merchants, and the Attestation of Compliance (AOC) for service providers.
Understanding the report
The report provides an overview of whether your organization is compliant with PCI-DSS. It identifies areas of compliance and non-compliance and provides a detailed description of the controls in place.
Post-report follow-ups
Post-report follow-ups involve implementing remediation strategies based on the findings and recommendations in the report. Regular monitoring of these remediation efforts is essential to ensure sustained compliance.
Maintaining PCI-DSS Compliance
Maintaining PCI-DSS compliance is an ongoing process that involves continuous monitoring, periodic auditing, and comprehensive employee training.
Continuous monitoring
Monitoring your cardholder data environment regularly ensures that any issues and vulnerabilities are promptly identified and addressed, keeping your organization aligned with PCI-DSS requirements.
Periodic auditing
Regular audits are essential to maintain PCI-DSS compliance, making them a critical aspect of any data protection strategy.
Employee training
Continuous employee education on PCI-DSS and cyber threats is an essential aspect of maintaining compliance. Employees can play a vital role in identifying and reporting potential threats, thereby keeping your business security top-notch.
Potential Hurdles and Solutions in PCI-DSS Audit
While handling a PCI-DSS audit, organizations may face several challenges, but with appropriate solutions, they can be navigated successfully.
Understanding common challenges
Some common challenges include outdated software, weak passwords, and unencrypted data transmission. Understanding these challenges and their potential impact on compliance is the first step to overcoming them.
Implementing necessary solutions
The solutions to these challenges include updating software regularly, enforcing strong password policies, encrypting data transmission, and implementing multi-factor authentication.
Seeking external help when required
In situations where internal resources or knowledge are inadequate, seeking external help from cybersecurity and compliance experts can streamline your path to compliance.
The Role of a Qualified Security Assessor (QSA)
A Qualified Security Assessor plays a crucial role in conducting a PCI-DSS audit and ensuring compliance.
Defining the role of a QSA
A QSA is a professional certified by the PCI Council to conduct PCI-DSS compliance audits. Their role is to assess your organization’s security infrastructure and practices, and guide you throughout the process towards compliance.
Selecting a QSA
Choosing the right QSA is critical. They should have the necessary certification, relevant industry experience, and a solid understanding of PCI-DSS requirements.
Communicating effectively with your QSA
Clear and continuous communication with your QSA helps to ensure a smooth audit process. Regular discussions about your systems, operations, and controls provide your QSA with the necessary details to conduct a comprehensive audit and produce a reliable report.
In conclusion, a PCI-DSS audit is an essential process for businesses that handle cardholder data. With adequate preparation, understanding of the process, and the guidance of a skilled QSA, organizations can achieve and maintain compliance, affording them legal protection, and earning them customer trust and loyalty.