In the realm of digital security, the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI-DSS) stands as a critical regulatory framework for companies dealing with cardholder data. The article “Understanding the Role of Automated Scanning in PCI-DSS Compliance” sheds light on the essential and increasingly prevalent role that automated scanning technology plays in adhering to these standards. Through this piece, you get a valuable insight into how automated scanning can significantly bolster efforts towards safeguarding sensitive data, thus enhancing your company’s PCI-DSS compliance stance.
Understanding PCI-DSS
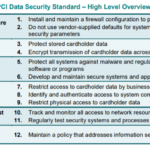
Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI-DSS) is a set of regulations established to ensure secure credit card transactions. These global standards apply to all entities that store, process or transmit cardholder data and are designed to safeguard sensitive cardholder data and prevent credit card fraud.
Definition of PCI-DSS
PCI-DSS is a universal security standard established by the Payment Card Industry Security Standards Council. Its primary function is to reduce credit card fraud by safeguarding cardholder data and promote a secure environment for transactions.
Requirements of PCI-DSS Compliance
To be PCI-DSS compliant, your organization must meet twelve key requirements that address critical security aspects including creating and maintaining a secure network, implementing robust access control measures, maintaining a vulnerability management program, regular monitoring and testing of networks, and upholding an information security policy.
Impact of Non-Compliance
Non-compliance with PCI-DSS can have severe consequences for businesses such as financial penalties, potential litigation, erosion of customer trust, and substantial reputational damage could occur. Non-compliant businesses are also at a greater risk of data breaches and credit card fraud, potentially crippling them financially.
Understanding Automated Scanning
Automated scanning plays a crucial role in information security, enabling businesses to promptly identify and address vulnerabilities in their systems.
Definition of Automated Scanning
Automated scanning is a process wherein a software tool scans systems for vulnerabilities, without the need for human intervention. It scans networks, servers, databases, web applications, and other resources to identify potential security gaps and weaknesses.
Processes in Automated Scanning
Automated scanning involves several phases, starting from scanning the target systems to analyzing the scan results. The process includes defining the scope, selecting the scanning tool, configuring the scan, executing the scan, analyzing the results, and finally, remediation of identified vulnerabilities.
Benefits of Automated Scanning
Automated Scanning offers many benefits such as detecting vulnerabilities in a timely manner, reducing manual work, increasing the repeatability and reliability of scans, and offering comprehensive coverage. It also provides informative reports that assist in the decision-making process.
Role of Automated Scanning in PCI-DSS
Automated scanning is a decisive tool for maintaining PCI-DSS compliance as it helps keep networks secure, protect cardholder data, manage vulnerabilities, and implement access control measures.
Maintaining Secure Networks
Through systematic inspection and detection of vulnerabilities, automated scanning helps maintain secure networks, a vital requirement of PCI DSS.
Protecting Cardholder Data
Automated scanning can discover security weaknesses that might enable unauthorized access to cardholder data, thus playing a key role in protecting cardholder information from potential threats.
Managing Vulnerabilities
Automated scanning aids in identifying, classifying, and prioritizing vulnerabilities based on their potential impact. This ensures vulnerabilities are addressed in a timely manner.
Implementing Access Control Measures
Automated scanning plays a significant role in enforcing access control measures by identifying loopholes that could allow unauthorized access, ensuring systems are only accessible to those authorized.
Types of Automated Scans
Various types of automated scans are used for different security needs. Some of these include vulnerability scans, intrusion detection scans, configuration compliance scans, and penetration tests.
Vulnerability Scans
Vulnerability scans identify potential vulnerabilities in the system. They help in detecting weaknesses that a potential attacker could exploit, such as outdated software, misconfigurations or unpatched systems.
Intrusion Detection Scans
Intrusion detection scans monitor network or system activities for malicious actions or policy violations and alert the system administrators to any suspicious behaviour.
Configuration Compliance Scans
This type of scan ensures that system configurations align with an enterprise’s defined security policy and regulatory requirements.
Penetration Tests
Penetration tests, or pen-tests, simulate cyber-attack scenarios on a system to identify vulnerabilities before they are exploited by malicious individuals.
Understanding Automated Scanning Tools
These are software developed to perform automated scans, helping businesses to comply with security standards such as PCI-DSS.
What are Automated Scanning Tools?
Automated scanning tools are software applications that automate the scanning process, assisting organizations in identifying system vulnerabilities. They range from vulnerability scanners to penetration testing tools and configuration scanners.
Effective Tools for PCI-DSS Compliance
A number of automated scanning tools are conducive for PCI-DSS compliance. Each tool has distinct functions and benefits and should be selected based on the unique needs of an organization’s process and systems.
Features of Effective Scanning Tools
An effective scanning tool should be capable of in-depth system analysis, profiling the entire IT infrastructure and providing continuous monitoring. It should also be able to produce clear, understandable reports that aid in effective decision-making.
Implementing Automated Scanning for PCI-DSS Compliance
Implementing automated scanning involves choosing the right tool, configuring the scans, and executing and monitoring the scans.
Choosing the Right Scanning Tool
Choosing the right tool is contingent on your organization’s needs and budget. It’s important to opt for a tool that fulfills your requirements and aligns with your IT environment.
Configuring Automated Scans
After selecting the tool, the next step is to correctly configure the scans. Incorrect configuration can lead to inaccurate results, so performance in real-world settings should be tested during this stage.
Executing and Monitoring Scans
Regular performance of scans is important to maintain PCI-DSS compliance. Monitoring is also crucial to review the scanning process and ensuring it functions properly.
Analyzing Scanning Results
Post scanning is the analysis phase, where results are reviewed to understand potential vulnerabilities and take corresponding remediation action.
Understanding Scan Reports
Identifying vulnerabilities involves understanding scan reports that provide details on the vulnerabilities discovered, including their severity and potential impact on the system.
Prioritizing Vulnerability Remediation
Based on the severity of the vulnerabilities detected, they should be prioritized for remediation. High-severity vulnerabilities with potential to disrupt system operations should be addressed first.
Following Up on Scan Results
The successful operation of an automated scanning process is followed up by correcting identified vulnerabilities and re-scanning to confirm their successful resolution.
Remediating Detected Vulnerabilities
Upon identifying vulnerabilities, remedial measures should be taken immediately. Remediation could involve patching, system configuration changes, or even hardware replacement.
Re-Scanning After Remediation
Once remediation tasks are completed, systems should be re-scanned to ensure vulnerabilities are fully resolved. Continuous re-scanning will further validate that new vulnerabilities have not been introduced in the remediation process.
Maintaining Continuous Scanning Processes
For comprehensive security coverage, maintaining a continuous scanning process is vital. A once-off scan may miss new vulnerabilities, hence the need for ongoing scanning processes.
Challenges with Automated Scanning
Automated scanning, while beneficial, comes with its share of challenges including handling false positives and negatives, managing large volumes of data, and ensuring timely remediation.
False Positives and Negatives
False positives are instances where the scanning tool flags a harmless element as a vulnerability, while false negatives occur when a tool overlooks a genuine vulnerability. Both scenarios are a challenge in automated scanning and need to be properly handled.
Handling Large Volumes of Data
Automated scanning can produce a large volume of data, which can be overwhelming to handle and analyze. A robust data management strategy is crucial for effectively managing this data.
Ensuring Timely Remediation
Organizations often struggle with timely remediation of vulnerabilities detected during scans. Delays in remediation can increase the risk of breaches, making prompt action necessary.
Best Practices for Automated Scanning in PCI-DSS
To fully leverage the potential of automated scanning in maintaining PCI-DSS compliance, certain best practices need to be followed.
Keeping Scanning Tools Updated
Outdated tools may overlook new vulnerabilities. Therefore, it is important to keep scanning tools regularly updated to ensure they can identify the newest threats.
Retaining Scanning Logs
All scanning logs should be retained for reference and future analysis. These logs serve as an audit trail and provide valuable insights during follow-up scans.
Regular and Random Scanning Schedules
To ward off the rapidly-evolving threat landscape, regular and random scanning schedules should be deployed. This approach optimizes the detection rates and ensures PCI-DSS compliance.
Ensuring PCI-DSS compliance through automated scans may seem complex and daunting. By selecting the right tools, using them effectively and maintaining a regular scanning schedule, you can improve your security posture and safeguard your business from potential threats.









[…] such as regular audits, network monitoring, penetration testing, vulnerability scanning, and staff training can greatly […]