“Overcoming Challenges: Best Practices for Dealing with a PCI-DSS Compliance Failure” arguably holds unrivaled significance in the current complex business landscape dominated by e-commerce. This article provides insight on the potential consequences of a PCI-DSS compliance failure and sheds light on effective strategies that can aid you in managing and mitigating the associated risks. The knowledge within offers a practical guide to help you navigate the often confusing realm of PCI-DSS compliance, making it an invaluable resource to any business navigating through this unavoidable aspect of e-commerce.
Understanding PCI-DSS Compliance
PCI-DSS compliance stands for Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard compliance. This is a global information security standard that was established by the Payment Card Industry Security Standards Council. The purpose of this standard is to encourage and improve cardholder data security, as well as to facilitate the broad adoption of consistent data protection measures globally.
Definition of PCI-DSS
The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI-DSS) is a set of security standards designed to ensure that all companies that accept, process, transmit or store credit card information maintain a secure environment. It provides a baseline of technical and operational requirements aimed at protecting cardholder data.
Importance of PCI-DSS compliance
PCI-DSS compliance is crucial for several reasons. One of them is to protect customer information and maintain trust in your business. If customers trust your organization, they are more likely to conduct business with you again in the future. If PCI-DSS compliance is not maintained, you put your customers’ information at risk of theft, which damages your reputation and can have financial consequences. Furthermore, not complying with PCI-DSS could lead to hefty fines from credit card issuers.
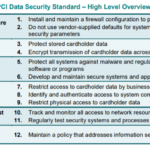
Components of PCI-DSS compliance
The PCI-DSS has 12 main requirements, which can further be divided into more specific rules. The requirements include building and maintaining secure networks, protecting cardholder data, maintaining a vulnerability management program, implementing strong access control measures and regularly monitoring and testing networks. A significant final requirement is maintaining an information security policy.
Identifying Signs of a PCI-DSS Compliance Failure
Identifying early signs of a PCI-DSS compliance failure is crucial in preventing data breaches. Here are few symptoms to look out for:
Unexpected system behavior
Unexpected system behavior, such as slower systems, frequent crashes, and abnormal data patterns, could possibly indicate that your systems are compromised. This could potentially pose a serious risk to PCI-DSS compliance.
Unusual customer complaints
If you start receiving unusual complaints from customers about unauthorized charges or attempts, this could be a sign of potential fraud or a compromise in your payment card systems. This must be taken seriously, as it can indicate a potential PCI-DSS compliance failure.
Warnings from security systems
It is essential to keep an eye on your security system’s warnings. If it is frequently reporting problems or intrusions, it’s vital to investigate immediately.
Inconsistent audit trails
Audit trails that show random or unexpected changes in patterns could suggest that unauthorized access is taking place. This can indicate that proper controls are not in place, potentially leading to a compliance failure.
Immediate Actions after Discovering Non-Compliance
Once a potential PCI-DSS compliance failure is detected, immediate action is necessary.
Immediate system analysis
The initial action required is an immediate system analysis. The organization needs to thoroughly review and assess their systems to diagnose the issues affecting compliance.
Engagement of a Qualified Security Assessor
Hiring an experienced Qualified Security Assessor (QSA) can help diagnose and remedy the issues effectively. A QSA is an individual certified by the PCI Security Standards Council to audit merchants for PCI-DSS compliance.
Notification of relevant stakeholders
Once non-compliance has been identified and confirmed, it is crucial to promptly notify all relevant stakeholders. This includes board members, regulatory bodies, and customers if their data is at risk.
Conducting a Thorough Investigation
To rectify the situation and prevent future non-compliance, a thorough investigation must be conducted.
Determining the root cause
The first step of the investigation is identifying the root cause of the non-compliance. This will offer relevant insight into how the issue occurred and what measures need to be considered to prevent recurrences.
Identifying affected systems and data
After establishing the root cause, affected systems and the extent of data that may have been compromised need to be identified. This allows for a concentrated effort into fixing the issue and prevents it from spreading to further systems.
Mapping out the extent of the non-compliance
Once the affected areas are identified, it’s crucial to map out the extent of non-compliance. This will help in formulating a corrective action plan and ensure that all areas of non-compliance are addressed.
Formulating a Corrective Action Plan
After understanding the context, severity, and root cause of a compliance issue, the next quest is creating an effective corrective action plan.
Setting appropriate goals
The corrective action plan should begin by setting realistic, measurable goals for rectifying the non-compliance issues. It’s important to ensure that these goals align with both the PCI-DSS requirements and the company’s business objectives.
Establishing new procedures
To achieve these goals, new procedures may need to be established. These procedures should be adequately communicated to employees and implemented effectively throughout the organization.
Implementing security measures
Enhanced security measures may need to be put into place to ensure future compliance. This can include stronger password requirements, new encrypted databases, or additional firewalls.
Implementing the Corrective Measures
After developing a corrective action plan, the next step is to actualize the devised remedies.
Reprogramming systems
In case the system programming was a part of the non-compliance, reprogramming or updating would be necessary. New systems offering better control and protection of cardholder data may need to be rolled out.
Implementing improved data control measures
Improving data control measures is vital. This can involve restricting access to sensitive data and ensuring that proper protocols are followed when dealing with cardholder data.
Enhancing the encryption and tokenization of data
Enhanced encryption and tokenization processes can help improve data security. Improvements in these areas are most often pivotal in achieving better PCI-DSS compliance.
Training and Educating Staff
Training and education play a critical role in the long-term maintenance of PCI-DSS compliance.
Organizing comprehensive training programs
Organizing regular, comprehensive training programs can help familiarize employees with PCI-DSS requirements and their roles in maintaining compliance.
Highlighting the importance of compliance
The training should underscore the importance of PCI-DSS compliance and the potential consequences in terms of financial penalties and reputational damage if compliance is not maintained.
Guidance on best practices
Staff must be guided on best practices for data safety and compliance. This incorporates secure password practices, ensuring secure networks, and verifying the suitability of customers’ systems.
Reevaluation and Monitoring
Regular reevaluation and monitoring of systems is necessary to maintain PCI-DSS compliance.
Regular system and procedure audits
Through regular audits, minor issues can be discovered before progressing into major problems. Implementing a schedule for regular audits is highly recommended.
Ongoing employee assessments
Regularly assessing employees’ adherence to new procedures and their understanding of PCI-DSS compliance helps to identify gaps that need additional training or resources.
Continual modification of compliance programs as needed
Just as data security threats evolve, so should the compliance programs. Adjustments and updates should be made as required to keep up with the evolving cybercrime landscape.
Engaging with Auditors
Engaging with auditors is a necessary part of maintaining PCI-DSS compliance.
Preparation for PCI-DSS audits
Preparation for PCI-DSS audits includes documenting all measures and procedures undertaken by the organization to achieve compliance. It also involves fixing any known issues ahead of time to avoid non-compliance findings.
Collaboration with auditors during the audit
While going through the auditing process, it’s essential to collaborate with and provide auditors with all information they might need. This improves the productivity of the audit and helps foster a good relationship with the auditors.
Implementing audit recommendations
After completion of the audit, the organization should strongly consider implementing the auditors’ recommendations. After all, auditors are experts in the sector and their recommendations can further improve data security measures.
Maintaining Long-Term Compliance
Achieving PCI-DSS compliance once is not enough. It is crucial to maintain compliance continually.
Regular system updates
Updates should be made regularly to software and hardware systems to keep up with the latest security standards. Outdated systems often come with known security vulnerabilities that can be exploited by malicious entities.
Continuous staff training
Maintaining compliance isn’t solely a technology issue; it’s just as much about the people who use that technology. Regular training updates can help keep employees aware of their responsibilities and educate them on emerging threats.
Strict adherence to new PCI-DSS developments and regulations
PCI-DSS standards are not static; they evolve over time to address new and emerging threats. Staying abreast of the latest developments will allow your organization to maintain its compliance status.
Conclusively, a PCI-DSS compliance failure may pose substantial challenges, ranging from reputational damage to possible financial penalties. Nonetheless, through a systematic approach encompassing immediate tactical actions, detailed investigation, vigorous corrective measures, staff training, and long-term vigilance and engagement, an organization can overcome these challenges and reestablish a secure, compliant environment that engenders customer trust.