Navigating the complex world of Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI-DSS) requirements can be a daunting task, especially when it comes to managing sensitive unencrypted data such as passwords. Your compliance with the PCI-DSS guidelines is pivotal for your organization’s cybersecurity health, and being equipped with the correct knowledge about password creation and management is instrumental to that end. In the article, “Understanding the Rules for Creating and Managing Passwords under PCI-DSS”, you will gain insights into the stringency and intricacies of these rules, giving you a head start in ensuring safeguard against potential threats to cardholder data.
Understanding PCI-DSS
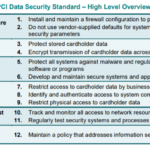
Definition of PCI-DSS
The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI-DSS) is a set of security measures developed to ensure that all companies that accept, process, store, or transmit credit card information maintain a secure environment. It was created by major credit card companies as a guideline to help make online transactions safer and decrease the risk of credit card fraud.
Purpose of PCI-DSS
The main aim of PCI-DSS is to protect cardholder data. It seeks to ensure that businesses handling that data use it in a manner that helps prevent fraud, hacking, and various other security vulnerabilities. The standard encompasses a wide range of aspects, including infrastructure, IT governance, access control, and password management.
Entities impacted by PCI-DSS
Any entity that deals with cardholder data is affected by PCI-DSS. This includes merchants of all sizes, financial institutions, point-of-sale vendors, and hardware and software developers involved in processing payments. They must all comply with the standards set by PCI-DSS to safeguard cardholder data.
Password Creation under PCI-DSS
Minimum password complexity requirements
PCI-DSS requires passwords to be complex and difficult to guess. A strong password typically contains a mix of upper and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters. These elements collectively help increase password entropy, making them more difficult for attackers to decipher.
The importance of unique passwords
Unique passwords are vital to maintaining a secure environment. Reusing passwords or variations of the same password across different applications can expose an entire system to vulnerabilities if just one application gets compromised.
Password length specifications
Under PCI-DSS, the minimum password length is seven characters. However, longer passwords are generally more secure. A combination of length, complexity, and uniqueness helps to create a robust password that is resistant to cracking attempts.
Mandatory use of special characters and numerals
PCI-DSS mandates the use of both numerals and special characters in passwords. Accordingly, it strengthens the password by enhancing its complexity and lowers the risk of successful brute force attacks.
Password Management under PCI-DSS
Password change frequency
PCI-DSS recommends changing passwords every 90 days. Regular password changes are essential in limiting the time window an attacker has to compromise a password.
Password history regulations
To prevent the recycling of previously used passwords, PCI-DSS requires that the last four passwords cannot be repeated. This discourages the reuse of old passwords and adds an extra layer of security.
Password storage security measures
Storing passwords securely is pivotal in maintaining a secure environment. PCI-DSS mandates that passwords should be stored in a form that is not easily deciphered. They must be stored in a hashed format and must not be displayed in plain text.
Key guidelines for securing password databases
Protection of password databases must be made a priority. Encryption and access control are crucial strategies for securing password databases. Access to these databases should also be strictly limited to prevent unauthorized access.
User Authentication and Identification
Building strong user authentication methods
Strong user authentication methods are essential in preventing unauthorized access. Multi-factor authentication, biometrics, and token-based authentication all contribute to strengthening user authentication.
Requirement for two-factor authentication
PCI-DSS requires two-factor authentication for remote network access. This helps prevent unauthorized access by requiring two forms of validation before granting access to the network.
Strategies for proper user identification
Proper identification of users is vital in preventing unauthorized actions. This can involve assigning unique IDs to users, monitoring activity logs to track user actions, and implementing strong access control policies.
Password Security Training and Awareness
Significance of education and training
An educated staff is one of the most effective security measures. Regular education and training on the importance of password security can largely reduce the risk of security breaches.
Best practices training for creating strong passwords
Training should include guidelines on creating strong passwords, the dangers of password reuse, the importance of regular password changes, and the risk of social engineering attacks.
Establishing a culture of password security consciousness
Building a culture of password security consciousness can go a long way in maintaining a secure environment. This means instilling in every individual the importance of their role in keeping the organization safe.
Vendor Default Passwords and PCI-DSS
Why vendor-supplied default passwords are unsafe
Vendor-supplied default passwords are commonly known and easily available, making them unsafe. They can expose a system to unwarranted risks if not changed.
PCI-DSS requirements on changing default passwords
PCI-DSS requires that all vendor-supplied default passwords be changed before installing a system. This step is vital in eliminating a common and easily exploitable security vulnerability.
The role of vendors in a secure password strategy
Vendors play an important role in secure password strategies. By providing unique passwords for each system and educating users on the dangers of default passwords, they can significantly contribute to improving security.
Remote Access and PCI-DSS Password Regulations
Additional password measures for remote access
Remote access introduces a new set of vulnerabilities. Thankfully, PCI-DSS has a set of measures to tackle them. These include requirements for a secure VPN, multi-factor authentication, and unique IDs for each user.
Two-factor authentication for remote network access
PCI-DSS requires two-factor authentication for remote network access. This adds an extra level of validation before granting access, thus making it more difficult for unauthorized users to gain access.
Challenges and solutions for secure remote access
Secure remote access poses significant challenges, such as the risk of unsecured networks and the difficulty in monitoring user activities. Solutions like encrypted communications, secure tokens for each session, and strict access control policies can be implemented to mitigate these risks.
Non-Compliance Risks and Consequences
Consequences of non-compliance with PCI-DSS password rules
Non-compliance with PCI-DSS password regulations can result in fines, increased transaction costs, and even the loss of the ability to process card payments. Additionally, it can lead to loss of customer trust and damage to the business’s reputation.
Potential impact on business operations and reputation
Violations of PCI-DSS can have far-reaching implications for businesses. They risk not only financial loss but also a ruined reputation and loss of customer trust, which can be even more detrimental in the long run.
Regular audits and assessments for maintaining compliance
Regular audits and assessments are fundamental to maintaining compliance with PCI-DSS. these can aid in identifying possible weaknesses in the system and taking steps to fortify them before they can be exploited.
Password Protection Technologies and PCI-DSS
Role of encryption in password protection
Encryption plays a crucial role in password protection. It is especially useful in protecting passwords during storage and transmission.
Exploring password management software
Password management software can significantly ease the process of creating and managing secure passwords. They also alleviate the problem of remembering complex passwords.
Advanced technologies for password security management
There are several advanced technologies available for password security management. Biometrics and token-based authentication are growing trends in this field.
Future Trends in Password Security and PCI-DSS
Adaptation to emerging password security trends
As security threats evolve, so will password security trends. Thus, PCI-DSS must continually adapt to these changes to keep cardholder data safe.
PCI-DSS security provisions for biometric passwords
Biometrics offers a higher level of security compared to traditional passwords. As biometrics becomes more prevalent, PCI-DSS is expected to develop provisions to regulate its use.
Predicting future changes in PCI-DSS password guidelines
Predicting future changes in PCI-DSS password guidelines can be somewhat challenging given the fluid nature of cybersecurity threats. Nevertheless, it is expected that the standard will continue to place high importance on secure password practices, and adapt to include emerging authentication technologies.