“Understanding the Main Objectives of PCI-DSS” is an insightful piece designed to enhance your comprehension of the central aim of the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI-DSS). By the end of this article, you will have gained essential awareness of the key goals behind PCI-DSS and why it’s instrumental in securing credit card transactions. It caters to those interested in understanding why it is vital in the business sector, particularly concerning safeguarding private data in electronic payment systems.
Understanding the Basics of PCI-DSS
The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI-DSS) is an information security standard for organizations that handle branded credit cards. In today’s digital world, keeping customer’s sensitive data secure is a prominent concern. Businesses of all scales use credit card details from their customers, making compliance with PCI-DSS a necessity.
Definition of PCI-DSS
PCI-DSS stands for Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard. This standard was designed to ensure that all businesses that process, store, or transmit credit card information maintain a secure data environment. By adhering to PCI-DSS, organizations can prevent credit card fraud, secure network vulnerabilities, and protect consumer’s sensitive data.
Origins and History of PCI-DSS
The standard was introduced in 2004 by major credit card companies including Visa, Mastercard, American Express, Discover, and JCB to provide a unified set of security measures. The objective behind this move was to prevent security breaches and standardize the protective measures across all companies that handle credit card data.
The Importance of PCI-DSS in Business Environments
In a business environment, PCI-DSS is crucial to secure cardholder data. It helps businesses to protect their customers’ sensitive information, thereby building trust and garnering reputation. Moreover, legitimate adherence to these standards can help a business avoid hefty fines associated with non-compliance.
Key Elements of PCI-DSS Standard
PCI-DSS Standard consists of key elements that clearly define the security obligations of the businesses.
PCI-DSS 12 Requirement Categories
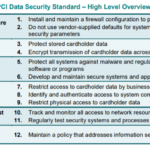
PCI-DSS framework consists of 12 core requirements categorized under six control objectives. These objectives range from the construction of a secure network, protection of cardholder data, network access control, to information security policy maintenance.
Roles and Responsibilities Under PCI-DSS
Under PCI-DSS, each entity involved has specific roles and responsibilities. These entities include merchants, service providers, and cardholder clients. The major role of these entities is maintaining a secure data environment and reporting their compliance status to the acquiring bank.
Control Objectives explained
The six control objectives serve as a guide for organizations to build and maintain a secure business network, protect cardholder data, establish a vulnerability management program, implement access control measures, monitor and test networks, and maintain a comprehensive security policy.

Main Objectives of PCI-DSS
PCI-DSS was designed to offer businesses a comprehensive checklist to follow in order to ensure maximum data security.
Build and Maintain a Secure Network
Building and maintaining a secure network involves installing and upkeeping a firewall configuration to safeguard cardholder data. It also includes not using vendor-supplied defaults for system passwords and other security parameters.
Protect Cardholder Data
Protecting cardholder data is central to PCI-DSS standards. This implies that cardholder information must be encrypted during transmission across open, public networks. Businesses must also take steadfast efforts to protect stored cardholder data.
Maintain a Vulnerability Management Program
Businesses need to maintain a vulnerability management program which involves the use of anti-virus software or programs. Further, they need to develop secure systems and applications.
Implement Strong Access Control Measures
Implementing strong access control measures means restricting access to cardholder data on a ‘need to know’ basis. Unique IDs must be assigned to each person with computer access, and physical access to cardholder data needs to be restricted.
Regularly Monitor and Test Networks
Business need to track and monitor all access to network resources and cardholder data. Regular testing of security systems and processes is also essential.
Maintain an Information Security Policy
Lastly, businesses must have a policy addressing information security and it should be disseminated amongst all personnel.
The Role of the Payment Card Industry Security Standards Council in PCI-DSS
The Payment Card Industry Security Standards Council (PCI SSC) plays a pivotal role in the maintenance and propagation of the PCI-DSS.
Development of the PCI-DSS Standard
The PCI SSC was responsible for the development of the PCI-DSS Standards. This council was established by the major credit card brands and was assigned with the task of managing the ongoing evolution of the Payment Card Industry (PCI) security standards.
Ongoing Administration and Management
The council is key to the ongoing administration and management of the PCI-DSS standards. They provide training and certification programs, maintain an environment to gather feedback from the participating organizations, issue updates and clarifications, and ensure that the standard remains robust and comprehensive.
Updates and Security
As the digital landscape is continuously evolving, so are the security threats. The council is responsible for regular updates to the PCI-DSS standards to fight any emerging threats. They future-proof the standards by meticulously analyzing new vulnerabilities and proposing amendments accordingly.

Understanding PCI-DSS Compliance
PCI-DSS compliance is all about meeting the standards set by the PCI SSC.
Who needs to be PCI-DSS Compliant
Any organization, regardless of its size, that accepts, transmits, or stores cardholder data is required to be compliant with PCI-DSS standards. This includes merchants, financial institutions, point-of-sale vendors, and hardware and software developers who work with credit card data.
Levels of PCI-DSS Compliance
There are four levels of PCI-DSS compliance, based on the volume of transactions processed by a business annually. Level 1 is for businesses processing over 6 million card transactions annually, while Level 4 is for businesses processing fewer than 20,000 card transactions per year.
Process of Achieving PCI-DSS Compliance
Achieving PCI-DSS compliance involves several steps. To start with, one needs to identify the data flow across an organization. Then, based on the identified flow, gaps need to be spotted against PCI-DSS requirements. The next step would be to address the gaps and re-assess. Lastly, the report needs to be submitted to the acquiring bank.
Benefits of PCI-DSS Compliance
Compliance with PCI-DSS doesn’t just help against data breaches but also offers several added advantages.
Increased Customer Confidence
PCI-DSS compliance helps businesses frequently handle customer card data with increased confidence. This, in turn, builds up customer trust, leading to more transactions and consequent profitability.
Avoidance of Security Breaches
Complying with PCI-DSS standards equips businesses to avoid potential security breaches. It provides a benchmark for what an organization should be doing to protect the sensitive cardholder data they handle.
Reduced Financial Risks
Non-compliance with PCI-DSS can lead to fines, penalties, or even the possibility of losing the capability to process card payments. Compliance reduces these financial risks significantly.
Challenges in Achieving PCI-DSS Compliance
Despite its manifold benefits, achieving PCI-DSS compliance has its own set of challenges.
Time and Resource Commitment
Achieving compliance requires a significant commitment of time and resources. Understanding the requirements and then implementing changes to meet them can be a daunting task.
Technical Challenges
The technical aspects of meeting PCI-DSS requirements can also be complex. It might involve changes in IT systems or in the way data is handled throughout the organization.
Continuous Compliance
PCI-DSS compliance is not a one-time event but requires continuous monitoring and management, which can be a challenge for organizations.
Potential Consequences of Non-Compliance to PCI-DSS
Non-compliance with PCI-DSS can have severe repercussions for businesses.
Financial Penalties
If a business fails to comply with PCI-DSS, it can be subjected to significant financial penalties from payment processors. These fines can range from a few thousand dollars to millions, depending on the level of non-compliance.
Reputation Damage
Beyond financial penalties, non-compliant businesses also risk severe damage to their reputation, which can have long-lasting impacts on customer trust and profitability.
Risk of Breaches and Data Theft
Without following PCI-DSS guidelines, businesses increase their risk of security breaches and data theft. This can result in fraud, identity theft, and even lawsuits or regulatory actions, leading to financial and reputational damages.
Case Studies of PCI-DSS Implementation
Case studies provide valuable insights into the practicality of PCI-DSS implementation.
Success Stories of PCI-DSS Implementation
Many businesses across various sectors have successfully implemented PCI-DSS. These success stories highlight the effectiveness of PCI-DSS in safeguarding customer data and instilling consumer trust.
Lessons Learned from Non-Compliance Cases
Case studies of non-compliance provide valuable lessons for other businesses. They serve as a reminder of the serious ramifications of not adhering to the standards, making a robust case for the necessity of PCI-DSS compliance.
Future of PCI-DSS
PCI-DSS is expected to evolve in response to the changing threat landscape and technological advances.
Evolving Threat Landscape
As cybersecurity threats evolve, the PCI SSC continually updates PCI-DSS to mitigate these threats effectively, helping businesses protect customer data better.
Expected Changes and Updates to the Standard
PCI-DSS will continue to be updated, with newer editions expected to introduce changes that reflect the evolving tech and threat environments. For businesses, staying informed and adapting to these changes is essential for maintaining compliance.
Increasing Importance of PCI-DSS in a Digital economy
With increasing digital transactions, PCI-DSS’s importance is only set to increase in the foreseeable future. As consumer data becomes more and more valuable, compliance with PCI-DSS will be crucial to ensure the trust and safety of customers.












[…] The main aim of PCI-DSS is to protect cardholder data. It seeks to ensure that businesses handling that data use it in a manner that helps prevent fraud, hacking, and various other security vulnerabilities. The standard encompasses a wide range of aspects, including infrastructure, IT governance, access control, and password management. […]