In the contemporary world of digital technology where data breaches have become alarmingly rampant, the implications for non-PCI-DSS compliant companies are particularly severe. The article, “The Consequences of Data Breach for a Non-PCI-DSS Compliant Company”, provides critical insights on the significant risks and the multitude of obstacles that a non-compliant organization can face in the event of a data breach. From hefty financial penalties to irreversible damage to your reputation, this article presents a comprehensive understanding of the potential aftermath.

Understanding PCI-DSS Compliance
Understanding PCI-DSS compliance is vital for any company that deals with credit or debit card transactions.
Definition of PCI-DSS
PCI-DSS stands for Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard. It’s a security standard that outlines the tangible steps that businesses need to follow to ensure secure management of cardholder data. The standard was developed and is maintained by the PCI Security Standards Council, a global consortium of the major card brands including Visa, MasterCard, American Express, and others.
The importance of PCI-DSS compliance
PCI-DSS compliance is important because it protects both businesses and consumers from the financial and reputational harm caused by data breaches. Compliance helps maintain trust in the payment system by safeguarding sensitive cardholder data. Non-compliance not only exposes businesses to severe penalties including fines, compensation costs, and litigation expenses, but also exposes cardholders to potential financial loss and identity theft.
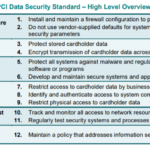
Prerequisites for PCI-DSS compliance
To achieve PCI-DSS compliance, a company must meet 12 requirements grouped into six high-level objectives covering network security, cardholder data protection, vulnerability management, access control measures, network monitoring and testing, and information security policy.
The Nature of Data Breaches
Understanding data breaches is a key aspect for any entity involved in the handling, processing or storage of sensitive data.
Definition and types of data breaches
A data breach is an incident where unauthorized individuals access, copy, transmit, or use data improperly. Data breaches can be categorized into different types, such as hacking where external actors infiltrate an organization, insider threat where data is breached from within, and accidental exposure where data becomes exposed unintentionally due to human error or system malfunction.
Main causes of data breaches
Data breaches can occur due to various reasons, including weak or stolen credentials, application vulnerabilities, improper data disposal, and malfeasance by a company insider. In many cases, these gaps in security can be due to lack of proper investment in cybersecurity, poor compliance with industry standards like PCI-DSS, or absence of robust data protection protocols.
The impact of data breaches on businesses
Data breaches can lead to severe operational, financial, and reputational consequences for a business. In addition to financial losses from fraud and penalties, a breach could lead to lost business opportunities, increased costs for security upgrade, and severe damage to a company’s reputation and customer trust.
Financial Consequences of Data Breaches for Non-PCI DSS Compliant Companies
Non-compliance with PCI-DSS can lead to significant financial losses for companies.
Fines and penalties from card brands and regulators
Companies that fail to comply with PCI-DSS could face hefty fines imposed by credit card companies and regulatory bodies. These fines vary depending on the extent and duration of non-compliance and the degree of negligence involved. Additionally, regulators could impose ongoing assessments until compliance is achieved and verified by a qualified security assessor.
Costs associated with fraud losses
Fraud losses represent one of the most direct financial impacts of a data breach. If sensitive cardholder data is compromised, fraudsters can use this information to make unauthorized transactions, leading to significant financial losses both for the impacted consumers and the involved businesses.
Expense relating to breach investigation and remediation
Data breaches also necessitate a thorough investigation to determine the extent of the breach, identify the vulnerabilities that were exploited, and develop a plan for remediation. These investigations can be costly, often necessitating the hiring of external experts. Remediation measures, such as security system upgrades or employee training, also add to financial burden.
Operational Consequences of Data Breaches
Beyond direct financial losses, data breaches can also result in operational interruptions.
Disruption of operations due to investigation
A data breach investigation often demands substantial time and resources, sometimes leading to disruptions in normal business operations. Depending on the severity of the breach, organizations may need to take certain parts of their network offline, causing further disruption.
Costs and time associated with system upgrades to prevent future breaches
In the aftermath of a data breach, companies typically need to invest significantly in strengthening their cybersecurity measures. This can include software and hardware updates, re-architecting networks, and implementing advanced intrusion detection systems. These upgrades can be costly and time-consuming, causing further operational interruptions.
Potential requirement to hire external consultants and specialists
Often, companies that have experienced a data breach need to bring in external consultants and specialists. This is not only to mitigate and recover from the incident, but also to identify, implement and validate the necessary improvements to their security processes and protocols. This can result in additional cost and operational impact.
Reputational Damage from Data Breaches
The impact of a data breach extends to a company’s brand and reputation.
Loss of customer trust
One of the most damaging outcomes of a data breach is loss of trust among customers. When businesses fail to protect sensitive information, customers may feel their trust has been violated and may discontinue their patronage, leading to lost revenue.
Negative public perception and media coverage
Data breaches often attract negative media attention, which can further harm a business’s reputation. Even after a breach has been contained, ongoing media coverage can prolong the crisis and continue to tarnish the company’s image.
Long-term impact on customer loyalty and retention
The reputational damage incurred from a data breach can have a long-term impact on customer loyalty and retention. Restoring trust following a breach is a long, arduous process which demands time, effort, and additional resources.
Legal Consequences of Data Breaches
Companies suffering data breaches may also face serious legal consequences.
Potential lawsuits from customers affected by the breach
Customers affected by a breach may seek legal redress by filing lawsuits against the company. Depending on the scale of the breach, lawsuit settlements or court-ordered compensation can amount to substantial sums, adding to the financial toll.
The possibility of facing criminal charges
In some cases, if a breach is found to be due to gross negligence or willful disregard for data security obligations, companies and their executives could potentially face criminal charges. This not only brings additional financial and reputational damage but can also result in imprisonment for the individuals involved.
Increased scrutiny from regulatory bodies and increased compliance requirements
A data breach can attract increased scrutiny from regulatory bodies, leading to more stringent oversight and potential increases in compliance requirements. This might include more frequent audits and higher standards for data protection, which can add to operational costs and complexity.
Impact on Business Relationships
The consequences of a data breach can also strain business relationships.
Loss of partnerships or alliances
If a data breach exposes not just a company’s data but also that of its business partners, it can irrevocably damage these relationships. This can led to the dissolution of partnerships or alliances, affecting business operations and growth.
Increased costs for cyber liability insurance
In the aftermath of a data breach, insurance companies may hike the premiums for cyber liability insurance, or even decline to cover a company that has suffered a major breach. This raises operational costs and increases financial risks.
Potential for loss of merchant account
In severe cases, especially where PCI-DSS non-compliance is a factor, a company might lose its merchant account, effectively disabling its ability to accept credit card payments. This can severely threaten a company’s ability to conduct business.
Consequence Management and Damage Control Strategies
Effective management of the aftermath of a data breach is essential to limit damage and restore operations.
Developing an effective incident response plan
An effective incident response plan is crucial in managing a data breach. A robust plan should include clear lines of communication, roles and responsibilities, strategies for containment and recovery, and protocols for dealing with legal authorities, regulators, and the media.
The importance of transparency and communication
In the wake of a data breach, transparency and open communication are key. Companies should promptly notify all affected parties, clearly explaining what happened and what steps are being taken in response, and providing advice on how individuals can protect themselves.
Investments in cybersecurity and PCI-DSS compliance
Preventing future data breaches often involves hefty investments in cybersecurity measures. Becoming PCI-DSS compliant is a crucial part of this, providing a framework to protect sensitive cardholder data and helping to regain customer trust.
Case Studies: Non-PCI DSS Compliant Companies Affected by Data Breaches
Several well-known companies have paid a heavy price for breaches brought about by non-PCI DSS compliance.
Retail chain Target’s 2013 data breach
In 2013, retail giant Target suffered a massive data breach that exposed the credit card information of approximately 40 million customers. The breach was traced back to malware installed on the company’s point-of-sale systems. As a result, Target incurred about $292 million in expenses related to the breach.
Yahoo’s 2013-2014 multiple data breaches
In 2013 and 2014, Yahoo experienced a series of data breaches that affected nearly all of its 3 billion user accounts. Stolen information included names, email addresses, birth dates, and in some cases, security questions and answers. The breaches knocked about $350 million off Yahoo’s Sale price when it was acquired by Verizon.
Equifax all-time massive data breach in 2017
In 2017, credit bureau Equifax announced that a data breach had exposed the personal information of 147 million people. The compromised data included names, Social Security numbers, birth dates, addresses, and some driver’s license and credit card numbers. Equifax has spent nearly $1.4 billion on cleanup and aftermath management for the breach.
Preventative Measures for Non-PCI DSS Compliant Companies
Prevention is the best defense against data breaches, and there are several preventative measures that companies can take.
Implementing a robust cybersecurity framework
A strong cybersecurity framework includes measures such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and encryption, along with robust access control measures and regular network monitoring and testing.
Encouraging employee training and awareness programs
Many breaches are caused by human error, making employee training and awareness critical. Employees should understand the potential risks and consequences of data breaches and be trained in best practices for data security.
The role of audits in identifying potential vulnerabilities
Regular audits are essential in identifying potential vulnerabilities that could lead to data breaches. These audits should include checks for compliance with industry standards like PCI-DSS, and should undergo a thorough assessment of all systems, networks, and processes.
In conclusion, the consequences of a data breach for a non-PCI-DSS compliant company can be severe and far-reaching. By understanding these potential repercussions, companies can better appreciate the importance of data security and PCI-DSS compliance.