In the realm of data security, the importance of an actionable and well-structured Incident Response Plan cannot be overstated, particularly when dealing with Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI-DSS) compliance. “Essential Elements for an Effective Incident Response Plan under PCI-DSS” provides a comprehensive breakdown of necessity in developing an incident response plan that not only meets PCI-DSS requirements but also ensures robust security and readiness against any data breaches or system compromises. Showcasing the impactful components with relevant illustrations, this article offers you critical insights and recommendations on how to construct an unassailable, efficient, and effectively compliant incident response plan.
Understanding the Importance of PCI-DSS
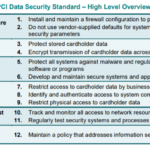
Overview of PCI-DSS
Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI-DSS) refers to a set of security standards that serves to ensure the safe handling of card data for businesses. It was established by major credit card companies to regulate the way businesses manage cardholder data and protect it from theft and fraud. The standards include network security, data encryption, access control, and ongoing monitoring procedures.
Significance of PCI-DSS for businesses
As an industry-standard, PCI-DSS compliance is critical for businesses dealing with credit card payments. Complying with PCI standards helps to protect your business from data breaches and potential financial penalties. Not only does it enhance your business reputation, but it also builds trust with your customers. Moreover, PCI compliance ensures that your business is maintaining proper cybersecurity measures to keep customer payment card data safe and secure.
Consequences of non-compliance with PCI-DSS
Failure to comply with PCI-DSS can result in serious consequences. In the case of a data breach, your business may be liable for financial losses suffered by customers or banks. You may also face significant fines and penalties from the credit card industry. Furthermore, your business may lose the ability to accept credit card payments, which can drastically affect your revenue. Finally, a data breach can severely damage your business reputation and result in the loss of customer trust.
Role of Incident Response Plan in PCI-DSS Compliance
Definition of incident response plan
An incident response plan is a set of procedures designed to identify, respond to, and recover from a security incident. The goal of an incident response plan is to minimize the impact of a security event on business operations and data integrity. This plan should provide clear instructions and establish roles and responsibilities for dealing with different types of incidents.
Value of an incident response plan in PCI compliance
In the context of PCI-DSS compliance, an incident response plan is extremely valuable. It allows businesses to respond promptly and effectively to a security incident that could compromise cardholder data. Incident response plans are specifically required by Requirement 12.9 of the PCI-DSS, which stipulates businesses must implement an incident response plan that addresses various notification and escalation processes.
How lack of an incident response plan can lead to PCI-DSS non-compliance
Without a properly structured incident response plan, your business runs the risk of non-compliance with PCI-DSS. Failure to effectively respond to a security incident can lead to exposed cardholder data and a breach of PCI-DSS requirements. Non-compliance can result in significant fines, sanctions, and potential loss of ability to process credit card payments.
Structuring an Effective Incident Response Plan
Key components of an incident response plan
An effective incident response plan comprises several key components. These include incident identification processes, clear roles and responsibilities, communication strategies, incident documentation, and consistent review and testing procedures. Other critical elements include remediation strategies to prevent future incidents and a robust recovery plan to restore normal business operations following an incident.
Steps to create an incident response plan
Creating an incident response plan involves several steps. Firstly, prepare by identifying potential incidents and defining clear roles and responsibilities. Second, develop a strategy for responding to and managing different types of incidents. Third, decide how your team will communicate during an incident and how information will be documented. Finally, regularly test and revise your plan to ensure its effectiveness.
Maintaining and Updating an Incident Response Plan
Regular maintenance and updates are crucial to the effectiveness of an incident response plan. Changes in business operations, technology, or personnel may require modifications to the plan. Additionally, after an incident, it’s critical to review the plan and update it based on lessons learned.
Roles and Responsibilities in Incident Response
Defining the incident response team
The incident response team’s makeup will vary depending on your business’s size and industry. It typically includes employees from diverse roles, such as security, IT, legal, public relations, and executive management. This team is in charge of executing the incident response plan and managing the fallout from a security incident.
Assigning Roles and Responsibilities
Certain roles are essential within an incident response team; incident response manager, security analysts, IT specialists, and communication personnel. The incident response manager oversees the entire process and ensures adequate communication throughout. Security analysts and IT specialists handle the technical aspects of identifying, containing, and recovering from an incident. Communication personnel manage internal and external communication about the incident.
Training of the incident response team
Thorough and continuous training is vital for the incident response team. Regular training sessions should be conducted, including role-playing scenarios, so that team members are prepared to respond effectively when an incident occurs. Team members should also be updated on changes in compliance regulations and threats.
Incident Identification and Reporting
Methods to Identify and Classify Incidents
There are numerous methods to identify and classify incidents, such as intrusion detection systems, log monitoring, and suspicious network traffic analysis. It is vital to classify incidents based on their severity and threat to the business operation.
Procedures to Report Incidents
Upon identifying an incident, reporting it is the next crucial step. The reporting procedures should be clear and simple to execute. Once an incident is reported, relevant details should be recorded, and the incident response team should be promptly notified.
Importance of Timely Identification and Reporting
Timely identification and reporting of incidents can significantly reduce the potential damage. Early detection allows the incident response team to react promptly, limiting the breach’s scope, reducing recovery time and costs, and maintaining the organization’s trustworthiness.
Incident Assessment and Prioritization
Tools and Techniques for Incident Assessment
Incident assessment involves determining an incident’s nature, scope, and potential impact. This process can be aided by various tools and techniques, such as network analysis tools, malware analysis, and digital forensics.
Processes for Incident Prioritization
Following the incident assessment, incidents should be prioritized based on the risk they pose to the organization. For instance, an incident involving cardholder data may warrant immediate attention compared to less sensitive data.
Deciding on Incident Response Strategy based on Assessment and Prioritization
After assessing and prioritizing the incidents, appropriate response strategies must be formulated. These could involve containment strategies, eradication practices, and recovery plans, depending on the incident’s nature and impact.
Incident Containment and Eradication
Strategies for Incident Containment
Incident containment strategies aim at limiting the scope of the incident to prevent further damages. This could involve isolating infected networks, disabling certain system functionalities, or changing access credentials.
Practices for Incident Eradication
Following containment, incidents must be eradicated. This could involve malware removal, system patches, or even full system restorations. The eradication process’s main aim is to eliminate the threat to restore the system’s trust factor.
Ensuring Minimal Impact on Business Operations and Data Security
Throughout the containment and eradication process, it’s crucial to limit any interruptions to business operations and protect any sensitive data from further exposure. This involves close coordination among IT, business, and communication teams.
Post-Incident Analysis and Remediation
Conducting Post-Incident Reviews
Once an incident is fully handled, a post-incident review should be conducted to assess the effectiveness of the response and identify areas for improvement. The review should cover how the incident happened, how well the team responded, and what could be done better in the future.
Lessons Learned and Corrective Actions
From each incident, there should be lessons learned and corrective actions to be implemented. These could include changes to policies, procedures or systems, and additional training requirements.
Improving the Incident Response Plan Based on the Analysis and Remediation
The insights gained from the post-incident analysis should be used to revise and improve the incident response plan. The ultimate goal is to improve the ability to respond to future incidents.
Communication during Incident Response
Communication among the Response Team
Effective communication within the incident response team is crucial in handling an incident. Clear channels of communication must be established, with updates regularly given to all team members.
Communication with Business Stakeholders
Keeping business stakeholders informed is also important. Without causing unnecessary panic, stakeholders need to be aware of the incident scope, potential impacts, and steps being taken to resolve the issue.
External Communication and Disclosure Requirements under PCI-DSS
PCI-DSS requires organizations to report any breaches involving cardholder data to the relevant parties, including card brands and acquirers. It’s important to have clear external communication procedures to comply with these requirements.
Testing and Refining the Incident Response Plan
Necessity of Testing the Response Plan
Testing the incident response plan is vital to ensure its effectiveness. Testing can reveal weaknesses in the plan or areas that need further clarification.
Methods for Testing Incident Response
Testing can be conducted in various ways, such as tabletop exercises, simulations, or drills. Regardless of the method chosen, the aim is to put the plan into action in a controlled environment.
Refining the Incident Response Plan Based on Test Results
Following the test, any identified challenges or gaps in the plan should be addressed. Regular refinement of the incident response plan ensures that it stays effective and relevant in a rapidly changing risk environment.