In “Essential Security Technologies for PCI-DSS compliance“, a meticulous examination of pivotal security technologies necessary for adhering to Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI-DSS) compliance is presented. Focusing on the indispensable tools and methods to achieve and maintain this critical compliance, the article casts a spotlight on their relevance, how they strengthen your digital environment, and why they should be a part of your cybersecurity strategy. The digital landscape is fraught with myriad threats but with the right knowledge and technology, your business can thrive securely in the face of continuous digital challenges.
Understanding PCI-DSS Compliance
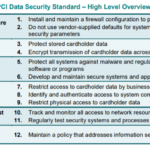
PCI-DSS, or the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard, is a comprehensive mandate that ensures all parties engaged in processing, transmitting, maintaining, and storing cardholder data employ and maintain secure systems and practices.
Definition of PCI-DSS
PCI-DSS is a global information security standard designed to secure credit card transactions against data theft and fraud. Companies accepting or processing payment card data must adhere to these standards. By maintaining compliance, companies safeguard the sensitive cardholder information they handle, thereby ensuring trust among consumers and stakeholders.
The purpose of PCI-DSS Compliance
The principle goal of PCI-DSS compliance is to protect the confidentiality and integrity of cardholder data throughout the transaction process. In the modern digital era, where data breaches are more common, compliance with PCI-DSS is crucial to guard against financial loss and damage to the reputation of the businesses involved.
Key principles and requirements of PCI-DSS compliance
The PCI-DSS standards are built on a framework of six key principles. These include a secure network and systems, protection of cardholder data, a vulnerability management program, access control measures, regular network testing, and information security policy. Understanding these key principles is the first step towards achieving and maintaining PCI-DSS compliance.
Firewalls for PCI-DSS Compliance
Firewalls play a pivotal role in the security strategy of organizations striving for PCI-DSS compliance.
Role of firewalls in data security
Firewalls provide a protective barrier between the organization’s internal network and the untrusted external networks. This technology scrutinizes incoming and outgoing network traffic and blocks the data packets based on a predetermined set of security rules, thereby protecting sensitive information.
How firewalls help achieve PCI-DSS compliance
PCI-DSS requirement 1 necessitates businesses to install and maintain a firewall configuration to safeguard cardholder data. Firewalls prevent unauthorized access, secure the network from malicious entities and activities, and sustain the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of cardholder data.
Choosing the right firewall for PCI-DSS compliance
Choosing a firewall compliant with PCI-DSS requirements involves considering the network size, systems complexity, and risk profile. Firewalls should be capable of inspecting and filtering the traffic and logging the activities for regular review. Organizations may need to seek assistance from security experts to make the appropriate selection.
Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS)
Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS) are integral to an organization’s comprehensive security setup and play a vital role in maintaining PCI-DSS compliance.
Basics of Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems
IDPS are software or hardware that monitor network activities for malicious actions or policy breaches and report such incidences to the management. They actively help protect a network by taking action against detected threats and blocking them from potentially causing harm.
The critical role of IDPS in PCI-DSS compliance
PCI-DSS requirement 11 states that businesses should use intrusion detection or intrusion prevention systems. This helps to timely identify and react to suspicious activities which can compromise cardholder data. With IDPS, organizations can safeguard their information systems from hacking attempts and various forms of cyber threats while ensuring PCI-DSS compliance.
Implementing an IDPS for PCI-DSS compliance
The first step in implementing an IDPS is conducting an organizational risk assessment to find the most beneficial system for the specific environment. It’s also vital to integrate the IDPS into the current security infrastructure effectively. Regular systems review and timely updates are equally important considering the evolving threat landscape.

Anti-Malware Technology
Dealing with malicious software is a prime concern for many organizations trying to achieve and maintain PCI-DSS compliance.
Understanding how Anti-Malware technology works
Anti-Malware technology is designed to prevent, detect, and remove malicious software from computing devices. These technologies generally perform real-time scanning for malware, schedule full-system sweeps, and automatic updates of the software itself to stay ahead of new threats.
Necessity of anti-malware in compliance with PCI-DSS
Under Requirement 5 of PCI-DSS, organizations are called to deploy anti-malware solutions on all systems commonly affected by such threats. Regularly updated antivirus or anti-malware software can combat the security threats and ensure the continuous protection of customer’s cardholder data.
Selecting a suitable anti-malware solution for PCI-DSS readiness
When selecting an anti-malware solution for PCI-DSS readiness, organizations must look for products that offer real-time protection, automatic updates, and thorough scanning capabilities. The selected software should cover all vulnerable systems, be interoperable with the existing IT environment, and be backed by dependable vendor support.
Secure Network Architecture
When striving for PCI-DSS compliance, organizations need to give due consideration to the security of their network architecture.
Definition and importance of secure network architecture
Secure network architecture refers to a planned and coordinated network design implemented with best security practices. The importance lies in the fact that it creates multiple layers of security. This layered approach ensures that even if one layer is breached, an intruder still has more layers to go through, thus adding more resilience to the overall security posture.
How secure network architecture supports PCI-DSS compliance
A secure network architecture reduces the risk associated with unauthorized data access and loss. PCI-DSS requirements clearly state that cardholder data environment should be protected from unauthorized access. Implementing a secure network architecture entails the use of firewalls, segregating cardholder data from the rest of the network, and encrypting data transmissions.
Designing a PCI-DSS compliant secure network architecture
When designing a PCI-DSS compliant secure network architecture, businesses need to define clear security rules and procedures for the network. This includes setting up firewalls properly, segregating network segments, securing wireless networks, and enforcing strong user authentication.
Data Encryption
As data traverses several systems and networks, a number of threats can compromise the confidentiality and integrity of these data. This is where encryption comes into play.
Overview of Data Encryption
In simple terms, encryption converts readable data (plaintext) into unintelligible text (ciphertext) through a process governed by an encryption algorithm. The encrypted data can only be deciphered using a decryption key.
The role of encryption in PCI-DSS data protection requirement
Under PCI-DSS, any cardholder data that is stored or transmitted needs to be encrypted. Encryption makes it difficult for anyone stealing the data to read it. Therefore, encryption is a valuable tool to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and security of cardholder data.
Implementing strong encryption for PCI-DSS compliance
For achieving PCI-DSS compliance, implement strong encryption technologies for cardholder data. Both at rest and during transmission. It is important to keep the decryption keys secure and away from the data they decrypt.
Tokenization
Tokenization is another method businesses use to secure credit card transactions and achieve PCI-DSS compliance.
Understanding the process of Tokenization
Tokenization is a process where a sensitive data element is replaced with a non-sensitive equivalent, known as a token, that has no exploitable or extrinsic value. It aims to minimize the amount of data a business needs to keep, which later reduces the business’s risk of handling sensitive data.
Why tokenization is crucial for PCI-DSS compliance
Tokenization is crucial for PCI-DSS compliance since it helps to considerably reduce the scope of applicable compliance requirements by rendering cardholder data useless to unauthorized individuals. It is a recommended solution for secure cardholder data storage.
Ways to apply tokenization to enhance PCI-DSS compliance
Tokenization can be applied in a way that cardholder data is never stored or processed by the merchant. Instead, the cardholder data is replaced with tokens upon transaction. It significantly cuts down on the amount of sensitive data in the system, which in turn improves security and helps maintain PCI-DSS compliance.
Access Control Systems
Access control systems are vital technology in ensuring the security of cardholder data.
Explaining Access Control Systems
Access control systems are technology platforms that control who can access particular areas or resources. They provide a method to authorize, authenticate, and account for users who are trying to gain access to a network resource.
Importance of Access Control Systems in achieving PCI-DSS compliance
PCI-DSS requirements call for limiting and monitoring access to cardholder data. Access control systems allow businesses to ensure that only authorized personnel can access sensitive data, thereby reducing the risk of data breaches and helping to maintain compliance.
Configuring Access Control Systems for PCI-DSS requirements
For maintaining PCI-DSS compliance, businesses should ensure that access rights are given on a need-to-know basis, users are authenticated, and access to system components is logged and reviewed. This way, organizations create a strong line of defense against unauthorized access to cardholder data.
Regular Systems Testing
Regular systems testing is crucial for maintaining a secure environment and achieving continuous compliance with PCI-DSS.
Why regular system testing is crucial for PCI-DSS compliance
Regular testing helps to ensure that systems and processes are working as intended and that gaps in security aren’t left undetected. Continuous vigilance is crucial to maintaining PCI-DSS compliance as cyber threats and vulnerabilities evolve over time.
Different system tests required by PCI-DSS
PCI-DSS mandates various testing mechanisms, such as vulnerability scanning, penetration testing, and the review of firewalls and routers. By conducting these tests, businesses can detect any weaknesses in their systems and rectify them before they turn into breaches.
Implementing efficient system testing processes for compliance
An effective testing process involves conducting regular reviews, employing a combination of automated scans and manual checks, and taking prompt corrective action whenever threats are detected. Businesses should document all testing activities and outcomes for audit purposes.
Secure Software Development Practices
Secure software development is pivotal in creating and maintaining a secure operating environment and achieving PCI-DSS compliance.
Need for secure software development in PCI-DSS
A secure software development life cycle ensures that security is integrated into every stage of the software development process. It reduces the number of vulnerabilities in the software and minimizes the risk associated with fraudulent activities and data breaches.
How secure coding practices support PCI-DSS compliance
Secure coding practices contribute to PCI-DSS compliance by reducing the risk of application vulnerabilities that can be exploited to gain unauthorized access to cardholder data. Requirement 6 of PCI-DSS emphasizes the need for secure coding practices.
Incorporating secure coding practices for compliance
Organizations can incorporate secure coding practices by educating developers about secure coding guidelines, performing code reviews, using code analysis tools, and conducting regular software vulnerability testing. It is also crucial to have an incident response plan in case of a security breach.