In this compelling article, “Understanding the Consequences of a Business Not Being PCI-DSS Compliant”, the spotlight turns onto those companies who disregard or overlook the dire implications of failing to comply with PCI-DSS. You will find a comprehensive exploration of the repercussions that can befall such businesses, providing invaluable insights into the potential risks, penalties, and long-term negative effects. This exposé will arm you with the knowledge to avoid common pitfalls and better align your business with necessary PCI-DSS compliance strategies.

Understanding PCI-DSS Compliance
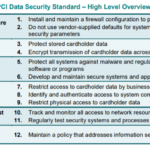
When it comes to handling customer payment information, there’s a universal standard businesses need to adhere to: the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standards (PCI-DSS).
Definition of PCI-DSS compliance
PCI-DSS compliance refers to following the standards set forth by the Payment Card Industry Security Standards Council. These standards have been designed to secure credit card data and other payment information from various forms of threats. Therefore, businesses that accept or process payment cards are required to be PCI-DSS compliant.
Reasons for becoming PCI-DSS compliant
Becoming PCI-DSS compliant is crucial for a business for various reasons. Primarily, it helps protect sensitive customer payment data from unauthorized access, thereby reducing the risk of financial fraud. Furthermore, compliance promotes trust among customers, as they can rest assured their data is being handled securely. In addition, avoiding penalties and maintaining a good reputation are also key advantages of compliance.
The process of becoming PCI-DSS compliant
The process to become PCI-DSS compliant involves several important steps. First, a business has to analyze its current payment card environment to understand the scope of compliance required. Following this, the business must implement requisite controls as per PCI-DSS guidelines to secure the cardholder data. Afterward, businesses need to undergo a validation procedure, often performed by an external Qualified Security Assessor, to confirm compliance. Lastly, businesses should continue monitoring and maintaining their PCI-DSS compliance.
Risks of Non-Compliance
Failure to comply with PCI-DSS can have severe consequences for a business and its customers.
Potential financial consequences
Non-compliance can trigger significant financial consequences, from fines imposed by payment card companies to potential liabilities caused by a data breach incident, which includes costs related to fraud losses, investigation, and customer notification.
Reputational damage risks
Non-compliance can result in severe damage to a business’s reputation. Customers and partners may lose trust in a company’s ability to protect their data, resulting in the loss of business and a decrease in market value.
Risks to customer trust and loyalty
The violation of PCI-DSS standards can potentially erode customers’ trust. When customers become aware of the inability of a business to secure their payment card data, they are likely to take their business elsewhere.
Legal Consequences of Non-Compliance
Beyond financial and reputational damage, the lack of PCI-DSS compliance can have serious legal implications.
Lawsuits and arbitrations
Businesses that are found to be non-compliant may face lawsuits from affected customers and payment card companies. These lawsuits can result not only in financial loss but can also be time-consuming and damaging to one’s reputation.
Fines and penalties
Upon a data breach, non-compliant businesses are subject to substantial fines by payment card companies as well as from federal agencies. Penalties can range from thousands to millions of dollars, depending on the size of the company and the magnitude of the breach.
Regulatory reviews and actions
Non-compliant businesses may also be subject to regulatory reviews and actions, including audits and investigations that lead to a further loss of time, resources, and business operations.
Financial Consequences of Non-Compliance
The financial impacts of non-compliance are not limited to fines and penalties; they can extend much further.
Monetary losses due to fraud
When payment card data is breached, businesses may have to compensate for fraudulent transactions, which can result in substantial losses.
Higher processing fees
Non-compliant businesses may face increased payment card processing fees, which can erode profits and add to operational expenses.
Loss of ability to handle credit card payments
In extreme cases, non-compliance may lead to businesses losing their ability to process credit card payments, severely affecting their business model, revenue, and customer relationships.

Technological Consequences of Non-Compliance
The technical ramifications of non-compliance can pose significant threats to business operations.
Potential for security breaches
Without the security measures mandated by PCI-DSS, businesses are highly vulnerable to cyber threats, including hacking and data breaches.
Increased vulnerability to cyber-attacks
Because non-compliance typically signifies weak data security infrastructure, such businesses may become attractive targets for cybercriminals.
Loss of important customer data
A security breach can lead to the loss of other important customer data, such as personal contact information, further compromising business-customer relationships and even potential legal trouble.
Impact on Business Reputation
Even the hint of non-compliance can spell trouble for a business’s reputation.
Customer perceptions of non-compliance
If customers perceive that a business is not adequately protecting their payment card data, they may choose not to do business with the company, leading to lost sales.
Media coverage and its effects
A data breach resulting from non-compliance can also attract negative media attention, which can harm the business’s reputation and further lead to losses in customer confidence and sales.
Long-term reputational damage
Such high-profile incidents can cause long-term reputational damage that could affect a business for years to come, making recovery slow and challenging.
Consequences for Business Operations
Non-compliance can significantly disrupt routine business operations.
Possible disruptions in daily operations
In the wake of a data breach, businesses may need to divert substantial resources to manage the fallout, causing disruptions in their day-to-day operations.
Impact on sales and profitability
The loss of customers’ trust, increased operating costs, and potential loss of the ability to process card transactions can all lead to reduced sales and profitability.
Risk of business closure
In the worst-case scenario, the compounding financial, operational, and reputational impacts of non-compliance can lead to business closure.
Impact on Customer Trust and Loyalty
Protecting customer data should be a top priority for businesses, and non-compliance can severely undermine customer trust and loyalty.
Perceived lack of data security
If customers perceive that a business does not prioritize data security, their trust can be severely compromised, potentially causing lasting harm to the customer relationship.
Loss of trust in the business
Even a single instance of non-compliance can mean long-term or permanent loss of customer trust, making it extremely difficult for businesses to rebuild these relationships.
Potential loss of loyal customer base
In many cases, non-compliance can lead to the loss of a loyal customer base, as customers may opt to do business with companies they view as more secure and trustworthy.
Case Studies of Non-Compliance
There are numerous examples of businesses facing severe consequences due to non-compliance.
Examples of businesses that have faced consequences
Some high-profile companies have faced significant fallout from non-compliance, such as hefty fines, legal action, and devastating damage to their brand image.
Lessons learned from these cases
These examples serve as important reminders of the risks associated with non-compliance and underscore the need for businesses to prioritize data security.
Strategies for prevention and recovery
These case studies also provide valuable insights into prevention strategies and recovery processes to help businesses avoid such incidents or recover swiftly and effectively should they occur.
Strategies for Ensuring Compliance
Fortunately, businesses can follow several strategies to ensure compliance.
Steps towards compliance
Becoming PCI-DSS compliant requires businesses to take numerous steps, such as conducting a thorough assessment of their payment card environment, implementing necessary controls, validating their compliance, and maintaining compliance regularly for long-term effect.
Benefits of regular audits
Regular audits are crucial for maintaining compliance. They help businesses identify any potential areas of weakness within their data security infrastructure and take preventative measures before any data breach occurs.
Importance of data security measures
Implementing robust data security measures is essential for maintaining PCI-DSS compliance. This could involve data encryption, secure network design, regular systems monitoring, or malware protection.
The role of employee training and awareness
Lastly, employee training and awareness play a significant role in ensuring compliance. It is essential that every employee understands the importance of PCI-DSS compliance, the proper handling of payment card data, and the potential consequences of non-compliance.
In conclusion, it’s evident how crucial PCI-DSS compliance is for the longevity and success of a business. Businesses must address any potential areas of non-compliance and invest in necessary resources to ensure the security of their customers’ payment card data. Being proactive in maintaining compliance can not only save a business from severe legal, financial, and reputational damage but also firmly establish it as a secure and trusted choice for customers.