From the perspective of data security and integrity, it is essential to comprehend the design and utility of the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI-DSS). This article aims to demystify PCI-DSS, elucidating its concept, importance and the specific entities it relates to. Therefore, whether you are a merchant, payment process entity, or simply an individual interested in the realm of data security, gaining clarity on PCI-DSS plays a pivotal role in safeguarding and ensuring compliance in credit and debit card transactions.

Understanding PCI-DSS
The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI-DSS) is a set of security standards designed to ensure that all companies that accept, process, store or transmit credit card information maintain a secure environment.
Definition of PCI-DSS
PCI-DSS, stands for Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard. This is a globally accepted set of policies and procedures designed to solidify credit, debit and cash card transactions and protect the cardholders against misuse of their personal information.
History and evolution of PCI-DSS
PCI-DSS was established in 2004 by the major card brands: Visa, MasterCard, Discover, AMEX and JCB. Initially, each card brand had its own set of security standards, but, they combined their individual programs into the PCI Security Standards Council (SSC). Over the years, the standards have evolved to meet the ever-changing landscape of data security, with the most recent update, Version 3.2, released in April 2016.
The significance of PCI-DSS in data security
PCI-DSS is significant in data security as it provides a baseline of technical and operational requirements designed to protect customer credit card data. It includes guidelines for encryption, access control, firewall configuration, and other measures to ensure that cardholder data is stored, transmitted, and processed securely.
Governance structure of the PCI-DSS
The PCI Security Standards Council (SSC) is responsible for the development, management, education, and awareness of the PCI-DSS. The council is governed by a set of representatives from the founding card brands, along with strategic members who contribute to the development of the standards.
PCI-DSS standards
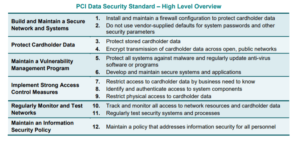
The PCI-DSS is based on a set of 12 requirements that are categorized into six control objectives.
Overview of the PCI-DSS 12 requirements
The 12 requirements of PCI-DSS include: securing the network, protecting cardholder data, managing vulnerability, implementing strong access control measures, monitoring and testing networks, and maintaining an information security policy.
Key attributes and standards
The key attributes and standards of PCI-DSS are broken into several different parts, including requirements for security management, policies, procedures, network architecture, software design and other critical protective measures.
Updates and enhancements in newer versions
The most recent version of PCI-DSS includes clarifications and additional guidance to help organizations understand the intent of requirements and how to implement them. It also includes additional requirements for service providers and changes to certain existing requirements.
Applicability of PCI-DSS
Despite being a requirement by the card brands, PCI-DSS applies to any organization that handles cardholder data.
Businesses/sectors that PCI-DSS applies to
Any business that processes, stores or transmits cardholder data is required to be PCI-DSS compliant. This applies across all sectors and industries, and includes both online and brick-and-mortar businesses.
Transactions that come under PCI-DSS
All card-present and not-present transactions, stored cardholder data, and transmission of cardholder data across public networks come under PCI-DSS.
Global applicability and recognition of PCI-DSS
PCI-DSS is globally recognized and accepted as the security standard for cardholder data. Any organization handling such data, irrespective of its geographical location, is required to be compliant.
Importance of Compliance
Non-compliance with PCI-DSS can have serious implications for businesses, affecting both their finances and reputation.
Risks associated with non-compliance
Failure to comply with PCI-DSS can result in hefty fines, increased transaction fees, loss of ability to accept card payments, and even business closure. Additionally, data breaches can result in loss of customer trust and damage to the business reputation.
Benefits of achieving PCI-DSS compliance
Compliance with PCI-DSS not only helps you avoid penalties and fines, but also safeguards your business against data breaches. It enhances customer trust and loyalty, reduces the risk of financial losses, and can give your business a competitive edge.
The role of PCI-DSS in reducing credit card fraud
PCI-DSS plays a crucial role in reducing credit card fraud by enforcing stringent controls around cardholder data. This helps in ensuring secure transactions and preventing unauthorized access to cardholder data.

Achieving PCI-DSS Compliance
Achieving compliance requires a structured approach, involving assessment, implementation of controls, and regular reporting.
Assessing your current state of compliance
Your first step towards achieving compliance is to assess your current state. This involves identifying any gaps in your security controls, understanding your cardholder data flows, and analyzing your vulnerability.
Implementing necessary controls and measures
Based on your assessment, you will need to implement necessary controls and measures to meet the PCI-DSS requirements. This may include network segmentation, encryption, access control measures, and developing security policies and procedures.
Reporting and validation processes
Upon implementing the necessary controls, you need to report your compliance to your acquiring bank and card brands. This usually involves a self-assessment questionnaire (SAQ) for small merchants, or a Report on Compliance (ROC) for larger ones, validated by a Qualified Security Assessor (QSA) or an Approved Scanning Vendor (ASV).
Roles and Responsibilities under PCI-DSS
Under PCI-DSS, various stakeholders have different responsibilities to ensure compliance.
Role of the merchant in ensuring compliance
The merchant is responsible for ensuring the security of cardholder data that is processed, transmitted or stored. They also need to ensure that all third-party service providers they use are also PCI-DSS compliant.
Role of payment processors in PCI-DSS
Payment processors are required to be PCI-DSS compliant and are responsible for the secure transmission of cardholder data. They are also required to validate their compliance annually.
Role of banks and financial institutions
Banks and financial institutions are responsible for ensuring that all merchants and service providers that they do business with are PCI-DSS compliant. They need to validate the compliance of these entities and report their compliance status to the card brands.
Challenges of Meeting PCI-DSS Requirements
Meeting the PCI-DSS requirements can be a challenging task for many businesses due to technical difficulties and organizational challenges.
Technical difficulties and solutions
Technical challenges include the complexity of credit card processing systems, the need for strong encryption and firewalls, and maintaining secure systems and applications. Solutions to such challenges involve investing in secure technology and infrastructure and partnering with experts who understand the complexities of securing cardholder data.
Organizational challenges and how to overcome them
Organizational challenges may include lack of awareness among employees about the importance of data security, lack of a dedicated security team, or resistance to change. Addressing these hurdles requires creating an organization-wide culture of security, providing continuous training and education to staff and leadership, and securing buy-in from all levels of the organization.
Understanding the cost and investment needed for compliance
Achieving PCI-DSS compliance generally requires a significant investment, including time, money, and resources. It’s important to understand that the cost of non-compliance (including potential penalties, loss of business, and harm to reputation) can far exceed the cost of implementing necessary controls and measures for compliance.
Audits and PCI-DSS
Regular audits are a critical part of maintaining PCI-DSS compliance.
The importance of regular audits
Regular audits allow you to review your security controls to ensure they are working as intended. They also help you to stay updated with the changing security landscape and adjust your standards accordingly.
The process of a PCI-DSS audit
A PCI-DSS audit typically involves reviewing your company’s security policies and procedures, inspecting physical security measures, assessing IT systems, interviewing staff, and conducting vulnerability scans and penetration tests. The audit results in an Attestation of Compliance (AOC) that verifies your company’s PCI-DSS compliance.
How to prepare for an audit
Preparing for a PCI-DSS audit involves reviewing your current security measures, ensuring your policies and procedures are up-to-date, preparing necessary documentation, and educating your staff about the audit process.
Training and Awareness
Education and continuous awareness are essential in maintaining compliance and protecting against security risks.
Importance of training and awareness programs for compliance
A well-designed training and awareness program can help educate employees about the importance of data security, the specific requirements of PCI-DSS and their role in maintaining compliance.
Key components of a PCI-DSS awareness program
A robust PCI-DSS awareness program should include training on data security policies and procedures, safe handling of credit card data, clear guidance on reporting potential security incidents, and regular updates on changing security requirements.
How to implement effective PCI-DSS training
Implementing effective PCI-DSS training requires designing relevant and engaging content, targeting all levels of the organization, using a variety of training methods, and establishing regular training schedules.
Future of PCI-DSS
As the digital landscape evolves, so will the challenges of data security.
Emerging trends impacting PCI-DSS
Emerging trends such as mobile payments, real-time analytics, and artificial intelligence pose new challenges for PCI-DSS compliance. Organizations will need to stay vigilant and adapt to these changes to keep their customer data secure.
Impact of technological advancement on PCI-DSS
Advancements in technology offer both opportunities and challenges for PCI-DSS compliance. While new technology can provide stronger security measures, it can also introduce new vulnerabilities that must be identified and addressed.
PCI-DSS forecast and predictions for future versions
Future versions of PCI-DSS are likely to include enhanced requirements for securing new payment channels, stricter controls for third-party providers, and increased emphasis on continuous monitoring and reporting. This continuous evolution of PCI-DSS will further secure the financial data and uphold the integrity of global payment systems.









[…] the intricacies of the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI-DSS) requirements for storing cardholder data can seem daunting. This article serves as a comprehensive […]